Alpheratz, designated as Alpha Andromedae, is the brightest star in the constellation of Andromeda, the celestial Chained Lady. It is also the brightest star in the Great Square of Pegasus asterism.
Key Facts & Summary
- Alpheratz is located at around 97 light-years / 29.7 parsecs away from our Solar System.
- It has an apparent magnitude of 2.06, however, Alpheratz is a binary star system composed out of a B-type star, which is the brightest, and an early-type A star.
- The primary star, designated as Alpheratz A, is also a mercury-manganese star whose atmosphere contains abnormally high levels of mercury, manganese, and other elements such as gallium and xenon. It is the brightest mercury-manganese star currently known, having a spectral type classification of B8IVpMnHg.
- Alpheratz is part of the famous asterism known as the Great Square of Pegasus. It is the upper left star of the asterism.
- The primary star has around 3.8 solar masses and 2.7 solar radii.
- Alpheratz A is 240 times brighter than our Sun and it is also 2.3 times hotter than our Sun, having surface average temperatures of around 13,800 K.
- This star is also a fast-spinning star having a rotational velocity of around 52 km / 32.3 mi per second, and it is also a young star with an estimated age of around 60 million years.
- The secondary star is smaller and less massive than the primary star. It has only 1.85 solar masses and around 1.65 solar radii.
- Alpheratz B is 13 times brighter than our Sun and it is also hotter having surface average temperatures of around 8,500 K.
- The secondary star is also a young star being only 70 million years old, and it is also a fast-spinning star with a rotational velocity of around 110 km / 68.3 mi per second.
- The Alpheratz star system has a radial velocity of -10.6 km / -6.5 mi per second.
- The best time to observe Alpheratz, the other stars, and deep-sky objects located in the constellation of Andromeda is during the month of November.
α Andromedae
Alpha Andromedae is known as Alpheratz and Sirrah, which derives from the Arabic name surrat al-faras, which translates to “the navel of the mare”.

The IAU approved the name Alpheratz for the star Alpha Andromedae in late 2016. Other Arabic names include al-kaff al-khadib and kaff al-nasir.
Formation
Alpheratz formed around 60 million years ago from an interstellar medium of gas and dust. Gravity pulled the swirling gas and dust together and resulted in the brightest star of Andromeda, Alpheratz.
The secondary star formed around 70 million years ago, however, it is unknown if the two stars were born from the same interstellar medium.
Distance, Size, and Mass
Alpheratz is located at around 97 light-years / 29.7 parsecs away from our Solar System. It is bright enough to be seen with the naked eye.

The primary star designated as Alpheratz A has around 3.8 solar masses, or 380% of our Sun’s mass, and 2.7 solar radii, or 270% of our Sun’s radius. It is thus more than 5 times bigger than our Sun.
The secondary star, designated as Alpheratz B has around 1.85 solar masses, or 185% of our Sun’s mass, and 1.65 solar radii, or 165% of our Sun’s radius. It is three times bigger than our Sun.
Other Characteristics
Alpheratz is a B-type star of spectral type B8IVpMnHg. It is classified as a mercury-manganese star which contains abnormally high levels of mercury, manganese, and other elements such as gallium and xenon being the brightest mercury-manganese star known.
The primary star has an apparent magnitude that slightly varies from magnitude 2.06 to 2.22. This star is 240 times brighter than our Sun and it has surface average temperatures of around 13,800 K. It is 2.3 times hotter than our Sun.

Alpheratz has a surface gravity of 3.75 cgs. This star is spinning fastly, having a rotational velocity of around 52 km / 32.3 mi per second.
The secondary star is an early-type A star of spectral type A3V. It is 13 times brighter than our Sun. This star is also 47% hotter than our Sun having surface average temperatures that reach 8,500 K.
Alpheratz B has it’s surface gravity recorded at around 4.0 cgs. This star is a fast-spinning star having a rotational velocity of around 110 km / 68.3 mi per second.
Star System
The two stars of the Alpha Andromedae star system orbit each other once every 96.7 days. There is also a visual companion in the line of sight of this star system. The visual companion has a magnitude of 10.8, and it is located at around 1,360 light-years away.
The Great Square of Pegasus
Alpheratz is the brightest star of the prominent summer asterism known as the Great Square of Pegasus. This asterism, apart from Alpheratz, contains three of the brightest stars in the constellation of Pegasus, namely Markab, Scheat, and Algenib.
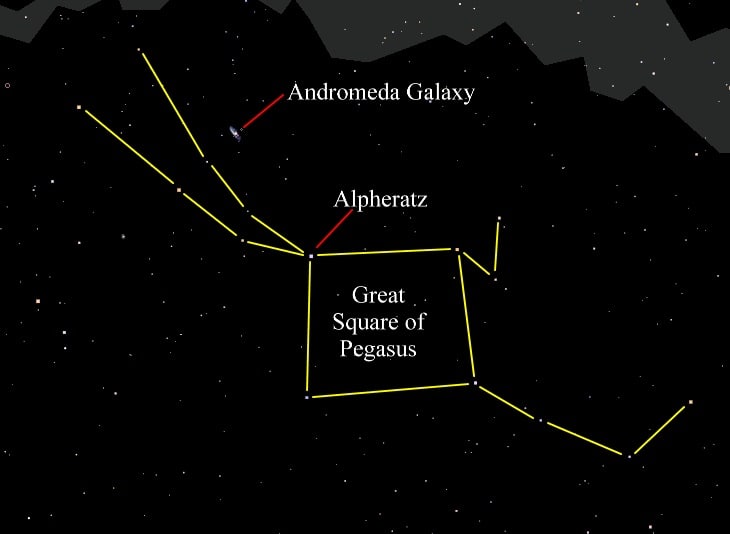
The Great Square of Pegasus is used by astronomers to find numerous famous deep-sky objects such as the Andromeda Galaxy, the Triangulum Galaxy, or the Great Pegasus Cluster, among many others. Alpheratz is also the closest star to us from this asterism.
Location
Alpheratz / Alpha Andromedae is located in the constellation of Andromeda. It is the brightest star in the constellation. The star can be seen from all locations north of the latitude 60oS.

The constellation of Andromeda is the 19th largest constellation in the sky. This constellation Is represented by the mythical princess who was the daughter of Cassiopeia and Cepheus and she was the wife of Perseus.
Andromeda is one of the first constellations listed by the famous astronomer Ptolemy, in his 2nd Almagest which contained 48 Greek constellations.
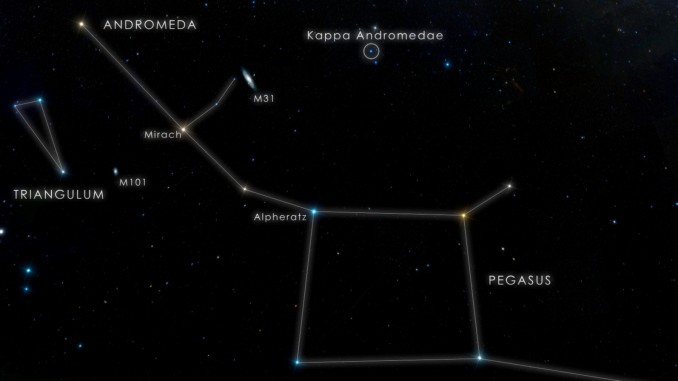
Andromeda contains many interesting deep-sky objects such as the Andromeda Galaxy / Messier 31, which is the nearest and largest galaxy to our Milky Way Galaxy, Messier 32, Messier 110, the spiral galaxy NGC 891, the planetary nebula NGC 7662 / the Blue Snowball Nebula, or the bright open star clusters NGC 752 and NGC 7686, among many others.
The 10 brightest stars in the constellation of Andromeda are Alpheratz, at magnitude 2.06, Mirach at magnitude 2.05, Almach at magnitude 2.10, Delta Andromedae at magnitude 3.28, Nembus at magnitude 3.57, Omicron Andromedae at magnitude 3.62, Lambda Andromedae at magnitude 3.8, Mu Andromedae at magnitude 3.87, Zeta Andromedae at magnitude 4.08, and Titawin at magnitude 4.10.

The best time of the year to observe the stars and deep-sky objects in the constellation of Andromeda is during the month of November. Alpheratz is prominent in the sky in the evenings from August to October while reaching it’s highest point in the sky at midnight on the 9th of October.
Did you know?
- In Hindu astrology, Alpheratz and Algenib form the 26th nakshatra known as the Uttara Bhadrapada.
- Alpheratz, Algenib, and Caph are known as the Three Guides. They mark the equinoctial colure, the prime meridian of the celestial spear that passes through the north and south celestial poles, and the two equinoxes (vernal and autumnal).
- The Chinese know Alpheratz as Bi Su er – the Second Star of Wall. The Chinese Wall mansion is formed by Alpheratz and Algenib, being one of the 7 mansions of the Black Tortoise.
- In medieval Arabic astronomy, Alpheratzis known as Al Ras al Mar’ah al Musalsalah – “the head of the chained woman”.
Sources:
Image Sources:
- https://www.star-facts.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/Alpheratz.jpg?189db0&189db0
- https://osr.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/04/alpha-andromedae-star.jpg
- https://astrologyking.com/wp-content/uploads/alpheratz-star-alpha-andromedae.jpg
- https://4.bp.blogspot.com/-XoNllvu5Ibg/WBnorVZQNOI/AAAAAAAAAXU/tWKjdM6KSbshAqeBe-QHhQWCRxNcyGCjwCLcB/s1600/Alpheratz.jpg
- https://i.pinimg.com/originals/8a/1c/b1/8a1cb16a64c70000dd037251c556d6a4.jpg
- https://www.astronomytrek.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/04/Andromeda_NASA.jpg
- https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/proxy/HbdQbgy0phIdrDZ97eqxRdg7PLi0dmWEMrpRnB9Sm1QaWcp9WF1B14VSy0y2huegEQNZczFAy2l2oCmPUnn-354ExVxulLNtFuL-yTbkRUXxVMd16unxCyZ3KNzlET0
