Bellatrix is the third brightest star in the constellation of Orion. It is a slightly variable star between the first and second magnitude. It generally varies between being the 27th and 25th brightest star in the night sky.
Key Facts & Summary
- Bellatrix has an estimated age of approximately 25 million years. It is old enough to consume its hydrogen supply at its core and evolve away from the main sequence into a giant star.
- Bellatrix has very high temperatures. On average, it is almost 4 times hotter than our sun at 22.000 Kelvin / 39.140 degrees Fahrenheit / 21.726 degrees Celsius.
- Because of its high temperatures, the star has a blue-white hue that occurs with B-type stars.
- Bellatrix is around 250 light-years / 77 parsecs away from our Sun.
- This star is a spectral type B2 III with a variable apparent magnitude between 1.59 and 1.64. Its absolute magnitude is -2.78.
- Based on this, the star’s general color is blue.
- Bellatrix is a massive star with about 8.6 times the Sun’s mass.
- Bellatrix has 5.75 solar radii – almost six times that of the sun, and it is around 9.211 times brighter.
- Its name is derived from Latin and it literally means female warrior.
- Bellatrix is one of the four stars used in celestial navigation. The other stars are Rigel, Betelgeuse, and Alnilam.
- It is one of the most easily recognizable stars, best seen in December and January. The star can be viewed with the naked eye.
- Bellatrix’s position in the constellation of Orion marks the giant’s western shoulder.
Since Bellatrix can be seen with the naked eye, it was known to humanity throughout the ages. One of the first accounts mentioning the star was in the works of the 9th-century Persian astronomer Abu Ma’shar. Later, translations occurred from Arabic into Castilian by John Seville in the 12th century.

The Persian astronomer applied Bellatrix’s name to the star Capella, but it was switched to Gamma Orionis by the Vienna school of astronomers in the 15th century.
Though now it is called Bellatrix which is Latin for Female Warrior, it was also called the Amazon Star – this comes from the Arabic name Al Najīd, which means The Conqueror. An even older Arabic name was The Lion.
Formation
Bellatrix formed from a nebula of gas and dust around 25 million years ago. Gravity pulled the swirling gas and dust into becoming what we now know as the Bellatrix star. Since it is enveloped in a growing outer shell of gaseous matter it has started to evolve off the main star sequence, and it is on its way on becoming a true giant.
Distance, Size, and Mass
When compared to the rest of the stars in the Orion constellation, Bellatrix is the closest to us at around 250 light-years / 77 parsecs away from the Sun.
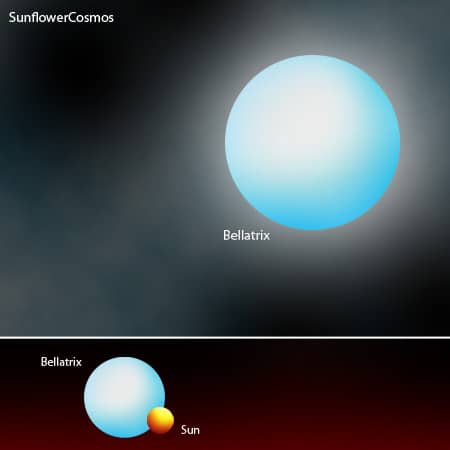
Bellatrix has 5.75 solar radii – it almost has six times our sun’s radius and almost twelve times its diameter. When compared to our sun’s mass, Bellatrix has 8.6 times more mass than our sun.
Other Characteristics
Due to its very high temperatures, almost 4 times hotter than our sun at 22.000 Kelvin / 39.140 degrees Fahrenheit / 21.726 degrees Celsius, the star has a blue-white hue that typically occurs with B-type stars.
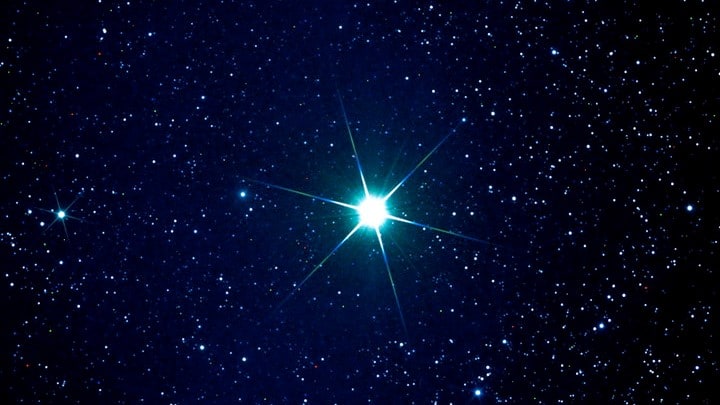

Also due to its high temperatures, Bellatrix emits light at a whopping 9.211 times the light of our sun. Though its variability in its visual magnitude is between 1.59 and 1.64, and its absolute magnitude is -2.78, thus making it between the 25th down to the 27th brightest star in the night sky, this is only because it is very far away.
If Bellatrix would be closer to us, it would clearly dominate the night sky. Recent studies suggest that Bellatrix is not a single star but rather consists of a binary system of two stars with similar properties but less luminous than a B2-type giant would be. However, no further evidence has backup up these claims.
Bellatrix’s visual variability makes it just a little fainter than Shaula in the constellation of Scorpius and Gacrux in Crux. It outshines Elnath which is in the constellation of Taurus, by just a tiny bit. The same applies to the stars Miaplacidus in the constellation of Carina, and its Orion neighbor Alnilam.
Location
Bellatrix is situated in the constellation of Orion - the hunter. It is the third brightest star after Rigel and Betelgeuse.
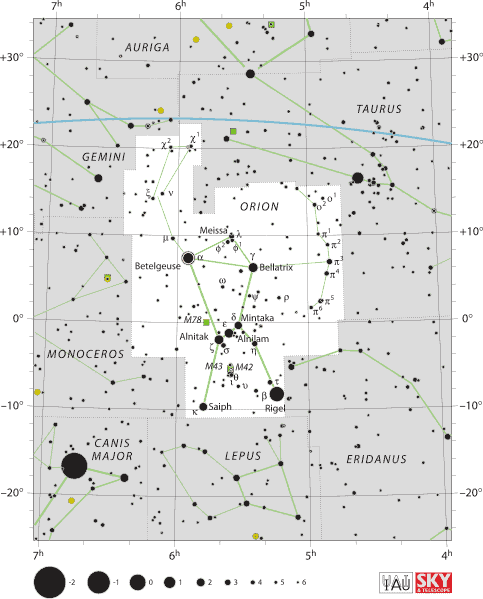
Bellatrix marks the left shoulder of Orion (appearing as the right from our perspective), while Betelgeuse marks the hunter’s right shoulder. Bellatrix is one of the seven bright stars that outline the celestial hunter’s familiar hourglass figure.
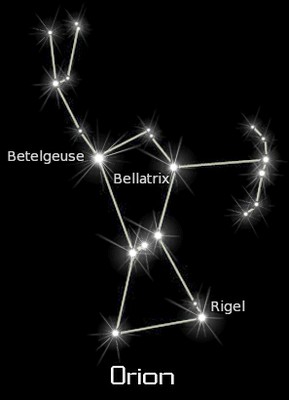
The Orion constellation as a whole is one of the most recognizable constellations in the night sky. It is known since prehistoric times and hosts two of the ten brightest stars in the sky, Rigel and Betelgeuse.
The Future
Since Bellatrix has started its transition in becoming a true giant, it is expected that Bellatrix will become an orange giant within a few million years. Since it has more than eight times the sun’s mass, it is also close to being considered a supernova candidate.
Did you know?
- Bellatrix is only 5 degrees west of the red supergiant Betelgeuse.
- Bellatrix along with Betelgeuse and Meissa also marks Orion’s head. They were considered the Euphratean Constellation of the King – Kabbab Sar – and were believed to bring good fortune, wealth, and military honors.
- The Inuit knew Bellatrix and Betelgeuse as Akuttujuuk – which translates to “those (two) placed far apart.”
- In the Northern Territory of Australia, the Wardaman people called the star Banjan. It symbolized the sparkling pigment used in ceremonies led by Unumburrgu – Rigel star – the Red Kangaroo Leader.
- Bellatrix has been mentioned in numerous works of fiction. Some examples are Planet of Apes and the Harry Potter franchise where one of the villains is a female character named Bellatrix.
- To the Chinese, Bellatrix was the Fifth Star of the Three Star constellation – an asterism which originally included Orion’s Belt stars Alnilam, Alnitak, and Mintaka. Later, the asterism expanded and more Orion stars were included.
- Bellatrix and the other stars of Orion can be best seen when the constellation dominates the evening sky in January.
- If Bellatrix were to replace our sun, everything on Earth would be burnt to a crisp and life would cease to exist.
Sources:
Image source:
- http://www.astronomytrek.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/03/Bellatrix.jpg
- https://earthandstarryheaven.files.wordpress.com/2015/03/025_bellatrix.jpg
- https://astrologyking.com/wp-content/uploads/bellatrix-star-gamma-orionis.jpg
- https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/f/ff/Orion_IAU.svg/483px-Orion_IAU.svg.png
- https://nieuws.kuleuven.be/en/content/2013/orion-black.jpg/image_preview
