Deneb Algedi, known as Delta Capricorni, is a multiple star system in the zodiacal constellation of Capricornus, the celestial Sea Goat. It is the brightest star in the constellation.
Key Facts & Summary
- The Delta Capricorni star system is composed out of three stars. Delta Capricorni Aa, Delta Capricorni Ab, and Delta Capricorni C.
- The star system is located at around 38.70 light-years / 11.87 parsecs away from the Sun.
- The primary star, Delta Capricorni Aa forms an eclipsing binary system with Delta Capricorni Ab. It is thus an Algol-type eclipsing binary system.
- The apparent magnitude of the star system is 2.81, and it varies from -2.90 to 3.05. The absolute magnitude has been determined to be +2.48.
- Since the star system is 2.6 degrees south of the ecliptic, it can be occulted by the Moon and rarely by planets.
- Delta Capricorni Aa is a white giant star of spectral type A7m III, thus the star has exhausted its hydrogen supplies.
- Delta Capricorni Aa is also a chemically peculiar Am star of spectral type kA5hF0mF2 III – under the revised MK system.
- This means that the star’s calcium K-lines matches the temperature of an A5 star, the hydrogen spectral type of an F0 star, and the metallic absorption lines of an F2 star.
- Delta Capricorni is also one of the 15 Behenian Fixed Stars. A group of stars used in medieval times in magic rituals.
- The primary star, Delta Capricorni Aa, has 200% of the sun’s mass and 191% of the sun’s radius.
- The temperatures detected on its surface are around 7.301 K. The star is also 8.5 times brighter than our sun.
- Delta Capriconi Aa has a rotation rate synchronous to its orbital period – quite an unusual feature for an Am star since they don’t spin so fastly.
- The rotational velocity of the primary star has been estimated at around 105 km / 65.2 mi per second.
Though Delta Capricorni is the brightest star of its constellation, it hasn’t been designated as the alpha star. However, many stars weren’t designated based on their brightness in the first place.

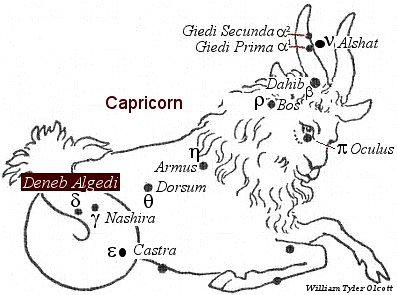
The traditional name of Delta Capricorni was Deneb Algedi. It is of Arabic origin and it translates to “the tail of the goat.” It has been named as such since its position in the sky marks the celestial tail of the Sea Goat. Many stars which mark their constellation’s tail have been named Deneb, or have a similar variation in their names.
Deneb Algedi / Delta Capricorni was one of the 15 Behenian Fixed Stars used in medieval times in magic rituals. These stars were associated with gemstones or plants, which were used in magic rituals to invoke the star’s influence. These magic stars also influenced astrology readings, being associated with planets.

In the case of Delta Capricorni, it was said to cause beneficence, destructiveness, sorrow, happiness, life and death. The star was associated with the planets Saturn and Jupiter, and with the chalcedony gemstone, and the marjoram plant.
Formation
Much of Delta Capriconi’s origin and formation are still unknown. The stars in the system may have formed at the same time or at different times and then they somehow ended gravitationally bound to one another. The stars aren’t associated with any known group of moving stars, but they likely formed from a molecular cloud of dust and gas. Gravity pulled the swirling gas and dust together to form the brightest star of Capricornus, Deneb Algedi / Delta Capricorni, and its companions.
Distance, Size, and Mass
The Delta Capricorni star system is located at around 38.70 light-years / 11.87 parsecs away from the Sun. It is one of the brightest stars in the night sky that can be seen with the naked eye.

The primary star is much bigger than our sun. Capricorni Aa has 2.0 solar masses or 200% of the sun’s mass and 1.91 solar radii or 191% of the sun’s radius.
The primary star’s closest companion, Delta Capricorni Ab, is much smaller than both the primary star and the sun. It has only 0.73 solar masses or 73% of the sun’s mass and 0.9 solar radii or 90% of the sun’s radius. The physical characteristics of the third star are currently unknown.
Other Characteristics
The primary star, Delta Capricorni Aa, is a white giant star of spectral type A7m III. The star has exhausted its hydrogen supplies at its core. It is also a chemically-peculiar Am star of spectral type kA5hF0mF2 III. This means that the star’s calcium K-lines matches the temperature of an A5 star, the hydrogen spectral type of an F0 star, and the metallic absorption lines of an F2 star.
Delta Capricorni is a fast spinner, having a rotational velocity at around 105 km / 65.2 mi per second. This rotation rate is synchronous to its orbital period – quite an unusual feature for an Am star since they usually don’t spin so fast.

The primary star has surface temperatures of around 7.301 K. It is thus 1.2 times hotter than our sun. Delta Capricorni Aa is also an energetic star, being 8.5 times brighter than our sun. The star has also been associated with extreme ultraviolet and radio sources, believed to be from the coronal activity of the secondary star. The surface gravity of the primary star has been estimated to be at around 3.66 cgs.
The secondary star is much smaller and in comparison much cooler than both the primary star and the sun. It has average surface temperatures of around 4.500 K. Delta Capricorni Ab is also believed to be a G-type of K-type star.
Stellar System
The primary and secondary stars have an orbital period of around 1.022768 days and their orbit eccentricity has been assumed to actually be 0.
The primary star, Delta Capricorni Aa forms an eclipsing binary system with Delta Capricorni Ab. It is an Algol-type eclipsing binary system. The apparent magnitude of the star system is 2.81, and it varies from -2.90 to 3.05. The absolute magnitude has been determined to be +2.48.
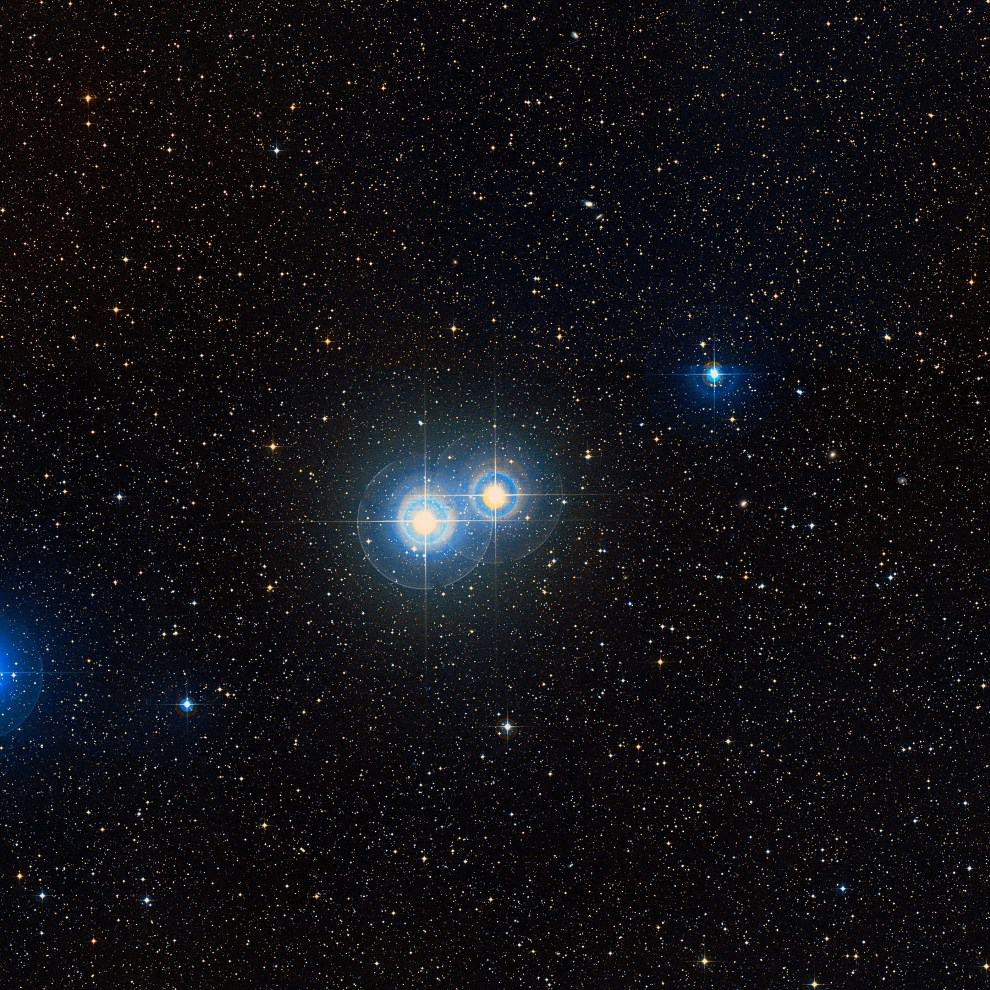

Since the star system is 2.6 degrees south of the ecliptic, it can be occulted by the Moon and rarely by planets. A 13th magnitude star has also been suggested to be part of the system, being at around two minutes of arc away.
The distance between these stars is increasing however, thus many aspects of the stellar system are questioned. The other component has been estimated to be at around one minute of arc away and is speculated to be a 15th magnitude star. The radial velocity of Delta Capricorni has been estimated to be at around -6.3 km / -3.9 mi per second.
Location
Delta Capricorni is located in the zodiacal constellation of Capricornus, the celestial Sea Goat. It mark’s the Sea Goat’s celestial tail.
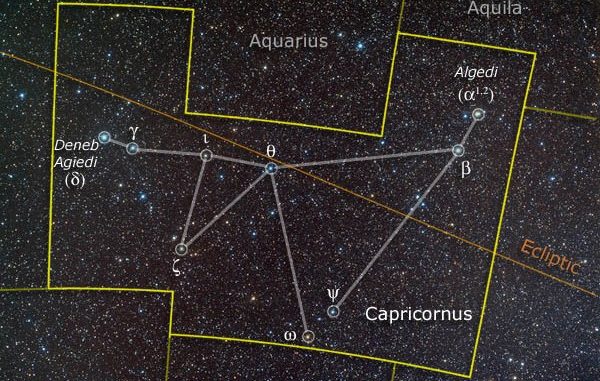
The constellation of Capricornus is actually the smallest zodiacal constellation. It is one of the 48 constellations recorded in the 2nd century by the Greco-Roman astronomer Ptolemy. Though the constellation can be seen with the naked eye, it is one of the faintest in the sky.
The Future
The primary star has exhausted its hydrogen supplies at its core and thus it is on its way in becoming a true giant, probably a red one. As its core will collapse the temperatures will rise and its outer layers will continue to expand.
Did you know?
- There are many galaxies, messier objects, and star clusters in Capricornus. The best time to view this constellation is during the month of July to November for observers in the northern hemisphere.
- The Chinese knew Delta Capricorni as the Fourth Star of the Line of Ramparts – referring to its presence in the Line Of Ramparts asterism.
- Delta Capricorni was occulted in the years 1962 and 1988.
- The star was included in a catalog of magnetic stars in the year 1958.
- In medieval astrology, the star was said to rule the blood vessels and nerve connections surrounding the vertebrae in the human body.
- The planet Neptune was first discovered near Delta Capricorni.
Sources:
Image source:
- https://www.astro.com/imwiki/de/thumb/Deneb_Algedi.jpg/300px-Deneb_Algedi.jpg
- https://cayelincastell.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/behenian-star-glyphs.jpg
- https://astrologyking.com/wp-content/uploads/deneb-algedi-delta-capricorni.jpg
- https://encrypted-tbn0.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcS_CHTk0eW7jKTwfgiPqT2FH7WQJ0D_VqoXzgV9S1vumxTRl3sWgQ&s
- https://www.constellation-guide.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/03/Algiedi-Alpha-Capricorni.jpg
- http://www.astronomytrek.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/Deneb-Algedi-Delta-Capricorni-600x381.jpg
- https://www.constellationsofwords.com/images/stars/dalgedi.JPG
