The First Quarter is a primary moon phase, along with the Third Quarter, the Full Moon, and the New Moon.
The First Quarter is also known as the Half Moon because 50% of its surface is illuminated by the Sun for a short period. Usually, it lasts for three nights.
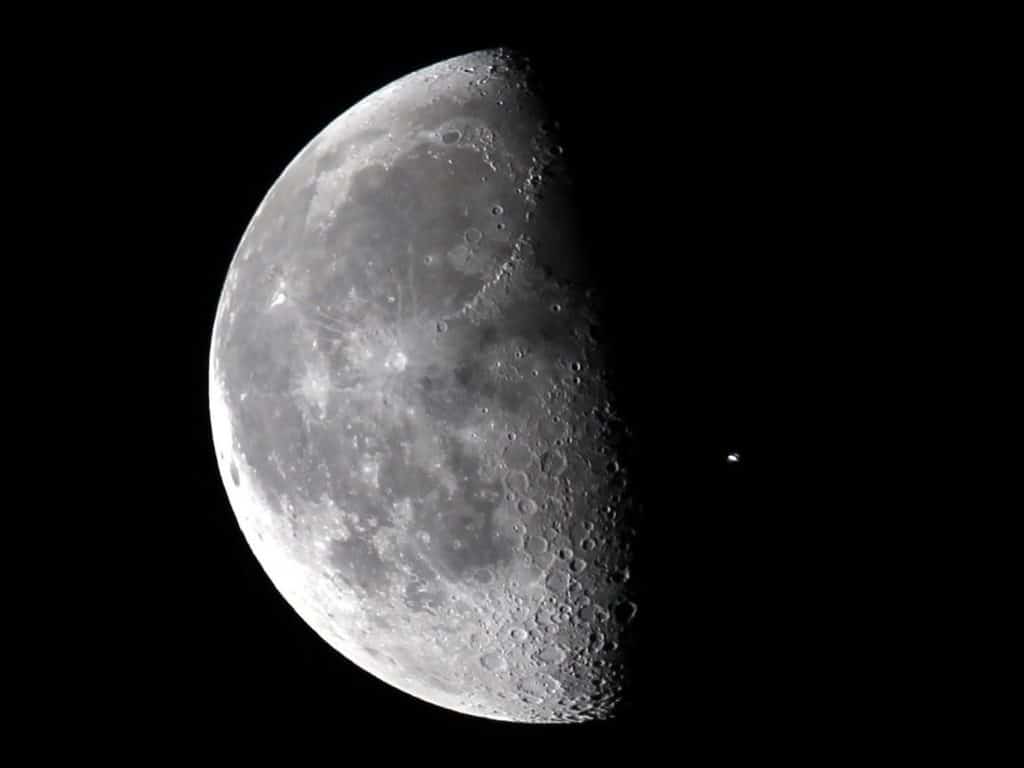

Each phase of the Moon has a significant impact on people and Earth. Let's find out how the First Quarter affects us and how this phase occurs.
What is the First Quarter?
The First Quarter is when we can see half of the illuminated part and half of the shadow part of the Moon. This is why generally, this phase is known as Half Moon. We can only see half and half because the Moon is at a 90-degree angle with respect to the Earth and Sun.
What's After the First Quarter?
The First quarter is the second primary phase of the Moon. It is followed by the Full Moon, while the first major phase is the New Moon and the last the Third Quarter.
The Full Moon occurs when the Sun and the Moon are aligned on the opposite sides of the Earth. In this phase, the Moon reaches its peak of illumination.
How does the First Quarter affect us?
The First Quarter is known as the growth period of the lunar month. The plans that we made during a New Moon are starting to take shape. This is a perfect time for learning new skills that will help you succeed in your projects. It is also a great time to connect with the Universe and the world around us.
Dreams tend to be more realistic under the First Quarter, and you may feel emotionally balanced. It is common in this period to have increased thirst or hunger.

An important thing we have to be aware of in this period is that we tend to bite more than we can chew, so we need to balance taking action and overdoing it.
During the First Quarter, men tend to be more exocentric, being the best time to focus on their work. For women, it is the most reasonable period. They tend to be more interested in discussing issues.
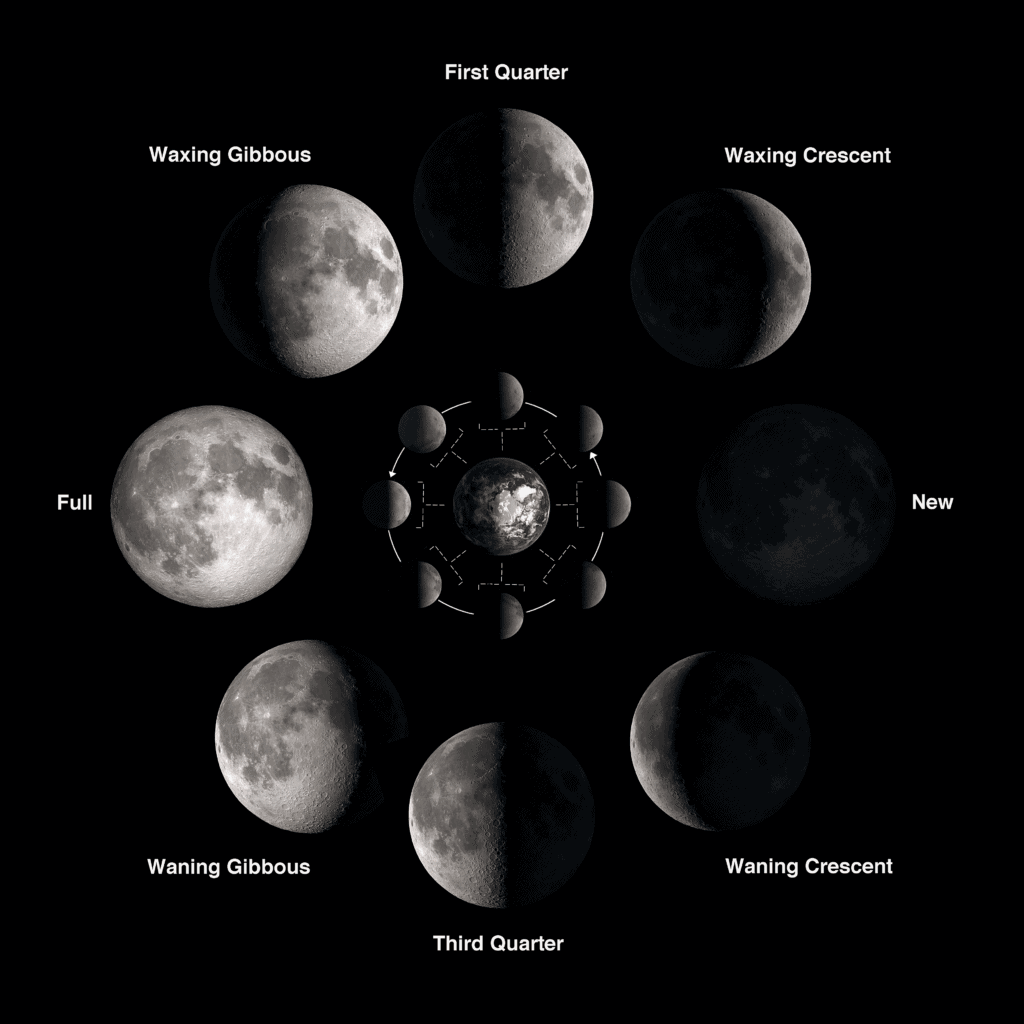
Moon Phases
When the Sun, Moon, and the Earth are aligned, and the Sun illuminates only the part of the Moon we cannot see, the Moon is at the minimum visibility, and it's called the New Moon.
When the Moon, Earth, and the Sun are almost aligned with the Earth in the middle, we can see the Moon's entire sunlit part. This is a Full Moon.
When the Moon is at 90 degrees angle with respect to the Earth and the Sun, we can see half of the sunlit part and half of the shadow part. This is the First and Third Quartes, also known as the Half Moon.
Between these phases, we have the Waxing crescent phase, the Waxing gibbous, waning gibbous, and the Waning Crescent phase.
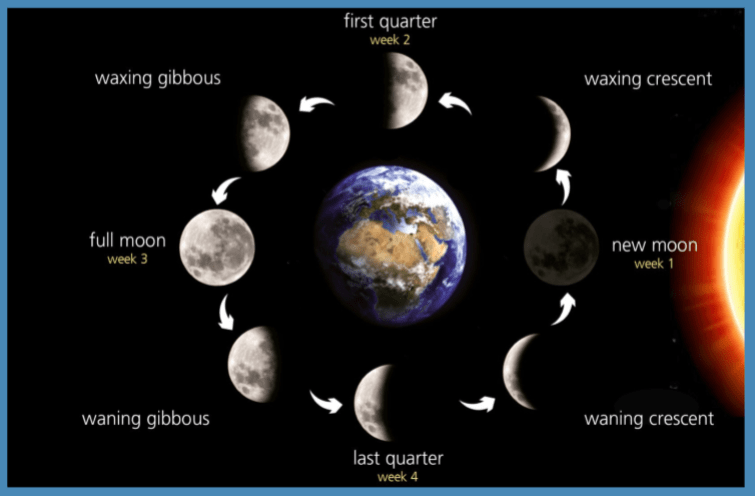
Waxing crescent happens after the New Moon when the Sun starts to illuminate the Moon, increasing its visibility, but less than half.
When the Moon visibility increases by more than half, it's called the Waxing gibbous phase.
The light starts decreasing after the full Moon, and until it reaches half of the Moon, it's called the Waning gibbous phase.
After the Third Quarter, light decreases until it fades completely. This is the Waning crescent phase of the Mood. If you want to check the actual phase of the Moon, you can find it here. If you are interested in its phase for tomorrow, click here, while yesterday's results are found here.
The First Quarter Calendar for 2020
Curious about when you can see the First Quarter phase of the Moon in 2020? Check out this list:
- January: From the 2nd until the 3rd with visibility between 44% and 63%, and on the 31st with a 36% visibility
- February: From the 1st until the 3rd with the visibility between 45% and 64%
- March: From the 1st until the 3rd with the visibility between 38% and 57%, and on the last day of the month, with visibility of 41%
- April: The first two night and the last two nights of the month, with the visibility between 36% and 62%
- May: On the 1st with visibility of 51%, and from the 29th until the 31st, with visibility between 43% and 66%.
- June: From the 27th until the 29th, with maximum visibility of 64%.
- July: From the 26th until the 28th, with minimum visibility at 39%, and maximum at 61%
- August: From the 24th until the 26th, with maximum visibility at 59%
- September: From the 23rd until the 25th, with visibility between 44% to 65%
- October: From the 22nd until the 24th, with the peak of visibility at 60%
- November: From the 21st until the 23rd, with maximum visibility of 63%
- December: From the 20th until the 23rd, with 65% maximum visibility.
The First Quarter Calendar for 2021
This is the calendar of the First Quarter phase for 2021, and the amount of visibility you can expect every month:
- January: From the 20th until the 22nd, with visibility between 37% to 65%.
- February: From the 18th until the 20th
- March: From the 20th until the 22nd, with maximum visibility of 59%
- April: From the 19th until the 21st, with maximum visibility of 63%
- May: From the 18th until the 20th, with visibility between 37% to 58%
- June: From the 17th until the 19th, with visibility between 43% and 65%.
- July: From the 16th until the 18th, with maximum visibility at 63%.
- August: From the 14th until the 16th, with maximum visibility of 60%.
- September: From the 12th until the 14th, with visibility between 35% to 58%.
- October: From the 12th until the 14th, with maximum visibility of 65%.
- November: From the 10th until the 12th, with a 61% maximum visibility.
- December: From the 10th until the 12th, with the peak of illumination at 65%.
Did you Know?
- The lunar cycle is 11 days shorter than a solar year. Every few years, lunar calendars add an extra month to keep on track with the seasons.
- The most spectacular time to watch the Moon is at moonrise. If you look at the east while the Sun is setting, when the Moon is close to the horizon, it will look more considerable than the surroundings. Because of the Earth's atmosphere, it will appear orange or yellow for a couple of minutes.
- The first man who hit a golf ball on the Moon was Alan Shepard in 1971 on the 6th of February.
- The Moon travels around the Earth at a distance of 1,423,000 miles (2,290,000 kilometers) with an average speed of 2,288 miles per hour (3,683 kilometers per hour)
- The surface of the Moon is approximately the size of Africa.
- We can only see one side of the Moon as it rotates around the Earth but its own ax as well. So it's the same side pointing at us, always.
- There are four kinds of lunar months:
- Anomalistic - 27 days, 13 hours, 18 minutes, 37.4 seconds. It's the period between one perigee and the next one.
- Nodical - 27 days, 5 hours, 5 minutes, 35.9 seconds. It is the time that it takes the Moon to pass through one node and return to it.
- Sidereal - 27 days, 7 hours, 43 minutes, 11.5 seconds. Using stars as a reference, that's how long it takes for the Moon to circle the Earth.
- Synodical - 29 days, 12 hours, 44 minutes, 2.7 seconds. This is the basis for most calendars we use today, and this is how we divide the year. The Moon circles the Earth in this length of time, using the Sun as reference.
Sources:
Image Sources:
- https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2010/06/Flying-Across-the-Moon1.jpg
- https://www.thoughtco.com/thmb/2aSpUkz-OuXmYb9Ha10b4oBxz44=/3728x3728/filters:fill(auto,1)/moon_phases-58b84a765f9b5880809d8d4d.png
- https://www.liveabout.com/thmb/shlX60hk1TVg-21WF1XpmD2oQ7A=/768x0/filters:no_upscale():max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/halfmoon-56e1bb3d3df78c5ba056a19f.jpg
- https://wsap.academy/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/Moon-phases.png
