Printable Alnilam Worksheets
Looking for fun activities to teach kids about Alnilam?
This premium worksheet bundle contains a printable fact file and 10 fun and engaging worksheets to challenge your students and help them learn about Alnilam.

Alnilam is one of the three stars which makes up the famous Orion's Belt asterism, which can be viewed in the night sky!
Key Facts & Summary
- Alnilam is also known as Epsilon Orionis, and it is the 4th brightest star in the famous constellation of Orion, the celestial hunter.
- Together with Mintaka, and Alnitak, Alnilam forms the asterism known as Orion's Belt.
- Alnilam appears as a single star to the naked eye. It is the biggest star out of the three which form the famous asterism. The second-largest star in Orion's Belt is Alnitak
- Alnilam is located at 1,975 / 600 parsecs away from the Earth.
- It is the 29th brightest star in the night sky!
- Alnilam is a blue supergiant star of spectral type B0 la. Its apparent magnitude is 1.69.
- This star is variable, and it belongs to the Alpha Cygni type of variable stars.
- Its brightness varies from magnitude 1.64 to -1.74
- Alnilam isn't just the biggest star in Orion's Belt; it is also the most massive. Also, the other two stars, Alnitak and Mintaka, aren't singular stars like Alnilam.
- In comparison to our Sun, Alnilam is a true giant! It is around 60 times bigger than our Sun, having 40 solar masses and about 32.4 solar radii.
- This star is 537,000 times brighter than our Sun, and it has powerful stellar winds that can reach up to 2,000 km / 1,242 mi per second.
- Since Alnilam has such powerful winds, it loses mass very fast!
- However, Alnilam is a young star, much younger than our Sun. Its age has been estimated to be at around 5.7 million years.
- Alnilam is much hotter than our Sun. It has surface average temperatures of around 27,500 K. Our Sun merely has 5,778 K.
- This blue supergiant is also a fast-spinning star. Alnilam rotates with speed between 40 to 70 km / 24.8 to 43.4 mi per second.
- It doesn't matter from where you are watching Orion's Belt since Alnilam is always located in the middle.
Alnilam Star for Kids
Alnilam is the biggest and most massive star, which is part of Orion's Belt. It is the star in the middle, and it is also very bright and varies in brightness over time.
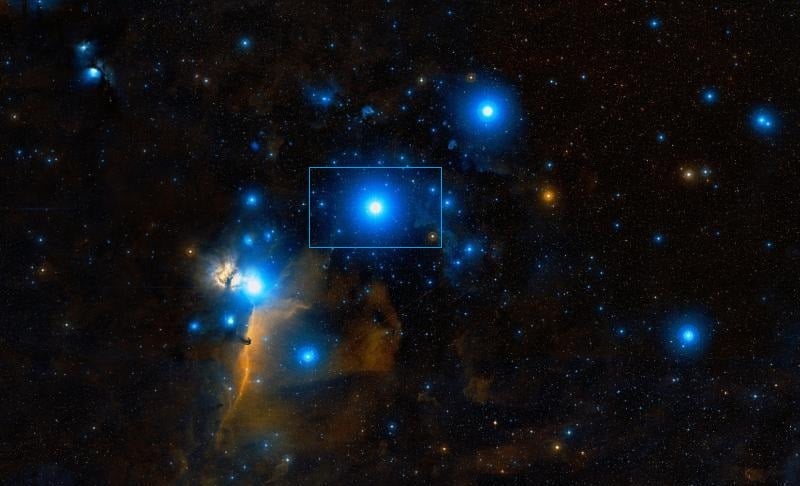

This giant star is also single, as the other stars, which form Orion's Belt, Mintaka, and Alnitak, are actually multiple star systems. Let's discover more about Alnilam!
Alnilam Characteristics
Alnilam is a blue supergiant star of spectral type B0 la. Its apparent magnitude is 1.69. However, it is an Alpha Cygni-type of variable star, hence the reason why its brightness fluctuates over periods, from magnitude 1.64 to -1.74.
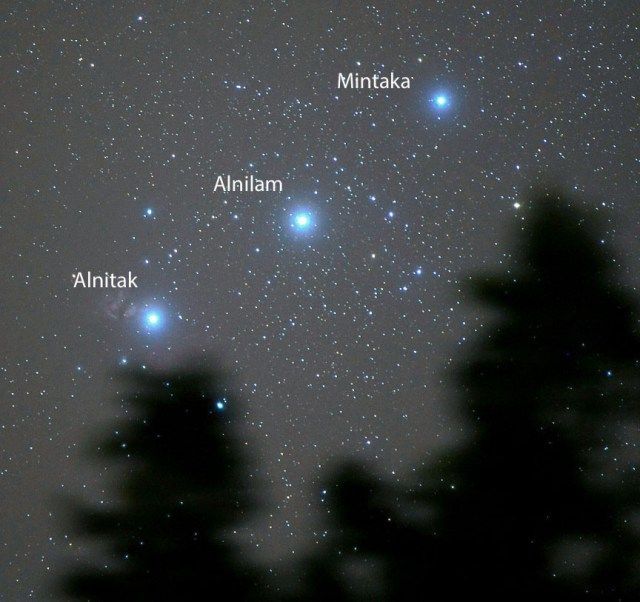

Alnilam is 537,000 times brighter than our Sun, and it has powerful stellar winds that can reach up to 2,000 km / 1,242 mi per second. This means that it is losing mass millions of times faster than our Sun.
This star is also very hot, having temperatures of around 27,500 K. It is more than 4.7 times hotter than our Sun. Alnilam is also a fast-spinning star, rotating with a speed between 40 to 70 km / 24.8 to 43.4 mi per second.
Formation
Alnilam formed around 5.7 million years ago from a rich interstellar medium of dust and gas. The constellation of Orion is famously known for its abundant molecular clouds of gas and dust.
Alnilam most likely formed in such a place, and since that spot was incredibly rich in materials, Alnilam ended up absorbing much of them. Gravity pulled the swirling gas and dust together and resulted in Orion's constellation's third brightest star and the central star of Orion's Belt, Alnilam.

Since Alnilam had a rich interstellar medium from which it formed, its life is also very short. Think about this; our Sun is more than four billion years old, while Alnilam is merely 5.7 million years old.
Alnilam won't exist for long in the near future due to its condition, and it will eventually explode as a supernova. With our current knowledge, we found out that Alnilam formed in the Orion Molecular Cloud Complex, which is a special place where many stars are born, but they are less than 12 million years old.
Fun Kids Facts About Alnilam
- Since Alnilam is so bright, it illuminates the nearby molecular cloud NGC 1990.
- The stellar winds of this star reach 2,000 km / 1,242 mi per second. It loses mass very fast.
- Alnilam is always the star located in the middle of Orion's Belt.
- Alnilam is also known as "Alnihan" or "Alnitam," and it comes from Arabic, translating to "the spring of pearls." This name refers to all of Orion's Belt stars.
- This star is located at 1,975 light-years away from us, a considerable distance, yet it is still among the sky's brightest stars.
Size and Comparison
Alnilam is the biggest and massive star out of all the stars forming Orion's Belt. The second is Alnitak, while the smallest is Mintaka. Alnilam has around 40 solar masses and 32.4 solar radii.
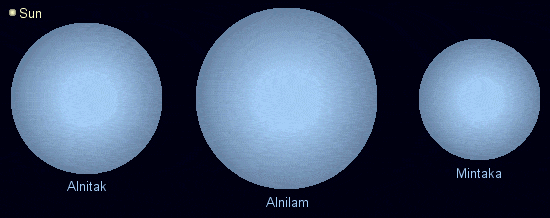
Alnitak, on the other hand, has 33 solar masses and 20 solar radii. Mintaka is at 24 solar masses and 10.4 solar radii. With that being said, Alnilam is more than 60 times bigger than our Sun.
Trivia
What is the Color of Alnilam?
Alnilam is a blue-white supergiant star of spectral type B0 la. It appears bluish-white in color, and blue colored stars are almost always among the hottest out there.
Are There Planets Around the Stars in Orion's Belt?
It doesn't appear that there are planets around the stars in Orion's Belt. Alnilam appears as a single lonely star; however, Alnitak and Mintaka have several other stars orbiting around them, forming stellar systems. Even so, there are slight chances that planets may indeed be around these stars. We have yet to discover them.
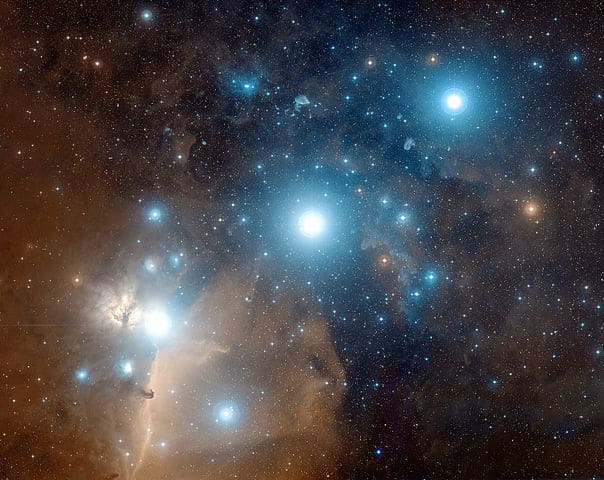

How Many Stars Does Orion's Belt Have?
To the naked eye, it appears that there are only three stars in Orion's Belt, namely Alnitak, Alnilam, and Mintaka. However, there are more than three stars here.
Alnilam is a single star, while Alnitak is comprised out of three stars, two of which are giant stars. On the other hand, Mintaka is a multiple star system, consisting of at least three stars.
Which is the Closest Star to us From Orion's Belt?
Mintaka is the closest star to the Sun from Orion's Belt, situated at 1,200 light-years. Alnitak is located at 1,260 light-years, while Alnilam is the farthest star in Orion's Belt, located at 1,975 light-years.
Alnilam Star Notes
- Alnilam is the biggest and most massive star in Orion's Belt. It is more than 60 times bigger than our Sun.
- This star is also the brightest and the only star without other companions.
- Alnilam is always the star in the middle of Orion's Belt.
- This star is the most farthest away from us out of the three stars in Orion's Belt; however, it is also the brightest.
Sources:
Image Sources:
- https://www.star-facts.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/Alnilam.jpg?189db0&189db0
- https://i.pinimg.com/736x/f8/1c/24/f81c24a22b1c1e1e70ae1d40565939d9.jpg
- https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/proxy/3q-aqKAKUsP9mo0iK7l67011Xhu1Vb0qF3r0cQua3DXwihoVW54yIdMHM7PUgpX68DAH3lmpi6JWZNUxN7eAgffxXlAEaTdVzQwK0Kdd2990Fcpo06ym8U4CxEL6qw
- https://nineplanets.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/Alnitak_Alnilam_Mintaka.gif
- https://nineplanets.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/Orion_Belt-1.jpg
