The Little Dipper is a famous asterism formed by the seven brightest stars of the Ursa Minor constellation. It is used to find the north pole star.
Key Facts & Summary
- The Little Dipper is usually confused for the entire constellation of Ursa Minor in the same way the Big Dipper is mistaken for the constellation of Ursa Major.
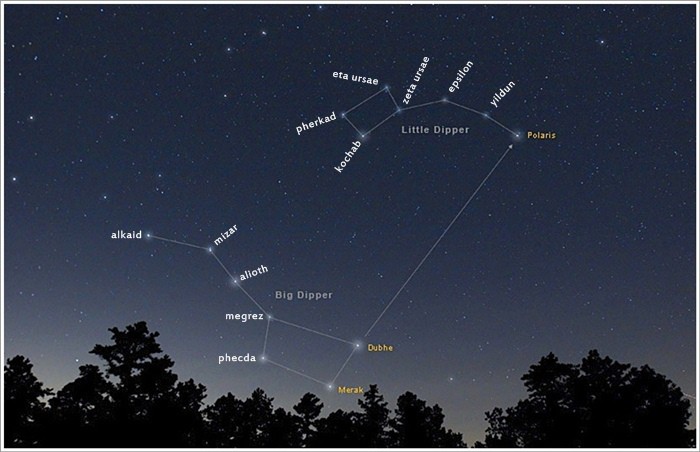
- There are seven stars that form the Little Dipper asterism, and they are Kochab, Urodelus, Yildun, Polaris, Pherkad, Ahfa al Farkadain and Anwar al Farkadain.
- Polaris is the brightest star of this asterism and the current North Star, revealing the North Celestial Pole's location.
- Sailors and mariners use the Little Dipper as a navigation tool for centuries.
- To find the Little Dipper, one must see the Big Dipper and follow straight up the line between Merak and Dubhe.
- The stars Kochab and Pherkad revolve around the North Star, and for that reason, they are called the Guardians of the Pole.
- The Little Dipper is located in the northern hemisphere, and it is visible between +90o and -10o.
- Many stars which are now part of the Little Dipper are former north pole stars.
- Its best to see the Little Dipper in June, during 9 pm / 21:00, since this is when the asterism is the most prominent in the sky.
- Ursa Minor was known as the Dog’s Tail or Cynosura before it was renamed under its current name.
- This constellation was created by Thales of Miletus around the year 600 BC.
- It was made out of a former constellation, which was known as Draco, the celestial dragon.
The Little Dipper for Kids
The Little Dipper is just as famous as the Big Dipper, especially since it contains the north pole star, Polaris. Many tales are associated with the Little Dipper, as it received great attention throughout the years.
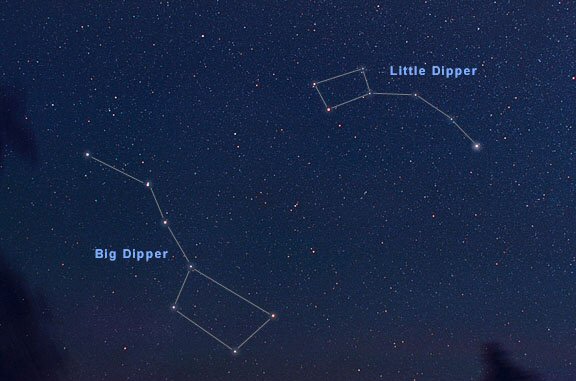
The Little Dipper should not be confused with the constellation of Ursa Minor, it is just a part of it. With that being said, let us see what is the Big Dipper, and which stars are part of it.
What is the Little Dipper?
The Little Dipper is an asterism made up of seven stars. It is located in Ursa Major, which spreads for over 256 square degrees in the sky, making it the 56th largest constellation. The asterism gets usually confused for the entire constellation, but we have to keep in mind that the Little Dipper is not and will never be a constellation.
Even though the brightest stars of Ursa Major form the Little Dipper, this asterism is not an exceptionally bright one. Besides its most shining star, Polaris, only two other stars, Kochab and Pherkad, can be seen from an urban area during nighttime.
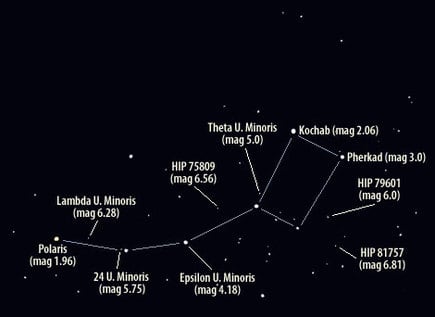
Three of its stars, namely Polaris, Yildun, and Urodelus, are known as "the handle" of the dipper, and the other four, Kochab, Pherkad, Anwar al Farkadain, and Akhfa al Farkadain, as "the bowl" or "the body." In the constellation of Ursa Minor, "the handle" of the Little Dipper forms the Little Bear's celestial tail, and "the bowl" is part of its flank.
Polaris is the brightest star of this asterism and the current North Star since it is near the celestial North Pole. It is a yellow-white supergiant with an apparent magnitude of 2.02, and it is located at around 433 light-years away from Earth. Polaris is also the 50th brightest star in the sky, and it is somewhere around 2,900 brighter than our Sun.
How Do you Find the Little Dipper?
In order to find the Little Dipper, you need to firstly find the Big Dipper. Once you have located it, continue the line between Merak and Dubhe upwards, and you will reach the North Star, which is the brightest star of the Little Dipper. Afterward, it will be easy to spot the entire asterism as it has a unique pattern.
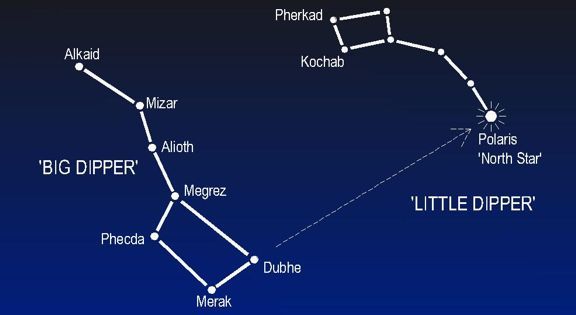
The distance from the Big Dipper and the bright star Polaris measures up to almost five times the distance between Merak and Dubhe. These two stars are also known as the Pointers because they point to Polaris's direction, thus to the direction of the North Pole.
Why is the Little Dipper Called the Little Dipper?
The Little Dipper gained its name because of its aspect. The asterism resembles a dipper, the same way the Big Dipper does. When you look at these two, they are the same, but they vary in size considerably, hence their names.
Where is the Little Dipper Located?
The Little Dipper is part of the constellation of Ursa Major, the 56th largest constellation in the sky. This constellation is located in the third quadrant of the northern hemisphere (NQ3), and it is visible between +90o and -10o.
The constellation of Ursa Major and thus the Little Dipper can be viewed best during June at 21:00 ( 9 p.m.), but even then, you need a clear sky and almost no light pollution.
Fun Kids Facts About the Little Dipper
- Long time ago, during ancient times, the Little Dipper was part of Draco the Dragon's constellation. The asterism formed this particular constellation's wings, but they were later clipped to create a new constellation – Ursa Minor. This happened somewhere around 600 B.C. when Thales, a Greek astronomer, encountered the seafaring Phoenicians.
They taught Thales how to use the stars of the Little Dipper for navigation. After this discovery, Thales decided to create the constellation of Ursa Minor to give the Greek sailors a new way to navigate by the stars.
- The stars Kochab and Pherkad are known as the Pole Guardians because it is believed that they protect the North Star.
- In 2014, it was discovered that the North Star shines two times brighter than it did two centuries ago and 4.6 times more luminous than in ancient times.
-The handle of the Little Dipper curves in the opposite direction of the Big Dipper's handle.
Size and Comparison
The Little Dipper is not a particularly large asterism, but it is a significant one. It is half the Big Dipper size, which means it covers about 10 degrees of the northern hemisphere.
Regardless of its relatively small proportions, the Little Dipper can be easily recognized in the night sky for its particular shape and its main star, Polaris.
Trivia
Big Dipper vs Little Dipper
The Big Dipper and the Little dipper are two similar asterisms, both in shape and importance. They reassemble two dippers or wagons, one larger and one smaller. Both of them are made up of seven stars, and since it is very easy to recognize their pattern, they were used as a point of reference, both on land and on water.
What is the Big Dipper?
The Big Dipper is an asterism, one of the most recognizable in the night sky, and its part of the constellation of Ursa Major. It consists of seven bright stars, with magnitudes that go from 1.8 to 2.4.
Its brightest star, Alioth, is 102 times brighter than the Sun and has a magnitude of 1.8. Two of its other bright stars are Merak, which shines 70 times brighter than our Sun, and Dubhe, which shines 415 times brighter than the Sun.
What is the Little Dipper Used For?
The Little Dipper is used mainly by sailors as its main star. Polaris indicates the north as it is the nearest bright star to the pole.
The North Star can also be used to find your latitude on Earth: if you are near the equator, Polaris will be near the horizon, but if you are at the North Pole, the star will be right above you.
Can You See the Little Dipper and the Big Dipper at the Same Time?
Both the Little Dipper and the Big Dipper are visible throughout the entire year in the northern hemisphere. As a result, they can be seen at the same time in the night sky. Although the Little Dipper is a little harder to spot since it doesn't have really bright stars, you need a clear sky to spot it.
Other Characteristics of the Little Dipper
The Earth axis is not fixed but strongly influenced by the Sun and the Moon; therefore, Polaris will not be at the North Pole forever. In approximately 14.000 years, it will change positions with Vega, and after another 14.000 years, Polaris will regain its title as the North Star.
Little Dipper Notes
- The Little Dipper is an asterism located in the constellation of Ursa Minor.
- This famous asterism, just like its bigger brother, is made up of the seven brightest stars in its constellation.
- These stars are Kochab, Urodelus, Yildun, Polaris, Pherkad, Ahfa al Farkadain and Anwar al Farkadain.
- Its most shining star, Polaris, is the current North Star.
-The Little Dipper has been used for centuries as a navigation tool.
- Former north pole stars are part of the Little Dipper.
- This constellation was created by Thales of Miletus around the year 600 BC. It was made out of a former constellation, which was known as Draco, the celestial dragon.
Sources:
Image Sources:
- https://legendsofthestars.weebly.com/uploads/1/7/5/0/17509023/2794715_orig.jpg
- https://ursaminorconstellation.weebly.com/uploads/1/5/5/3/15539188/1979920.jpg?436
- https://nineplanets.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/The-constellation-of-Ursa-Minor.jpg
- https://cdn.mos.cms.futurecdn.net/D4qstyCYkFVbk2FZoxvu5Y.jpg
- https://workhomeunion.com/universe/little-big-deeper.jpg
