Vega is the fifth-brightest star in the night sky, and it is the brightest star in the northern constellation of Lyra.
Printable Vega Worksheets
Looking for fun activities to teach kids about Vega?
This premium worksheet bundle contains a printable fact file and 10 fun and engaging worksheets to challenge your students and help them learn about Vega.
Key Facts & Summary
- Vega is located at only 25 light-years / 7.68 parsecs away from the Earth.
- Vega is designated as Alpha Lyrae, and it is a blue main-sequence star of spectral type A0V.
- This star is variable. It changes its brightness from magnitude -0.02 to +0.07.
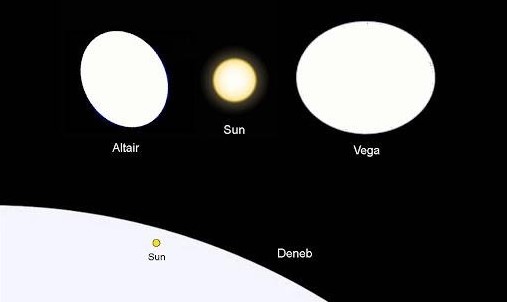
- Vega is bigger than our Sun, having 2.135 solar masses and around 2.362 solar radii. It is thus almost five times bigger than our Sun.
- Vega is 40.12 times more luminous than our Sun.
- The surface average temperatures on Vega have been recorded at 9,602 K. It is much hotter than our Sun.
- This star is considerably younger than our Sun, having an estimated age of around 455 million years.
- Around the year 12,000 BC, Vega was Earth's northern pole star.
- In the year 13,727, Vega will once again be the northern pole star.
- Vega is rotating very fast at its equator, having a velocity of around 236 km/s – 146.6 mi/s.
- Because of this tremendous rotational speed, Vega is bulged at the equator.
- Unlike other stars, Vega is a singular star, and it doesn't appear to host planets.
- Vega was the first star to be photographed, and it is also the first to have its spectrum recorded.
- Vega was photographed as early as 1850.
- A circumstellar disk of dust surrounds this star.
- Very few stars have the occasion of becoming the north pole star. Vega is one of these lucky stars, but Polaris is the current north pole star.
- Many stars that have an infrared excess because of dust emission are termed Vega-like stars.
Vega Star for Kids
The star Vega is the fifth brightest celestial object in the night sky, and it is also the most shining star in the constellation of Lyre. Because it is the brightest star there, Vega is also known as Alpha Lyrae.

Though Vega is a main-sequence star, in the future, it will become an M-class reg giant star. This may happen in the next 500 million years. Though it currently isn't a north pole star, Vega will replace Polaris as the north pole star in around 10,000 years.
Vega Characteristics
Vega is a blue main-sequence star of spectral type A0V. It is located at only 25 light-years / 7.68 parsecs away from the Earth. This star is variable. It changes its brightness from magnitude -0.02 to +0.07.
Vega is 40.12 times more luminous than our Sun. The surface average temperatures on Vega have been recorded at 9,602 K. It is much hotter than our Sun, almost twice as hot.
Around the year 12,000 BC, Vega was Earth's northern pole star. In the year 13,727, Vega will once again be the northern pole star, replacing Polaris.

Vega is rotating very fast at its equator, having a velocity of around 236 km/s – 146.6 mi/s. Because of this tremendous rotational speed, Vega is bulged at the equator. Unlike other stars, Vega is a singular star, and it doesn't appear to host planets.
Vega was the first star to be photographed, and it is also the first to have its spectrum recorded. It was photographed in 1850. A circumstellar disk of dust surrounds this star, and stars that have an infrared excess because of dust emission are termed Vega-like stars.
Formation
Vega is considerably younger than our Sun, having an estimated age of around 455 million years. Our Sun, for comparison, is 4.5 billion years old.
Vega formed out of an interstellar medium of dust and gas. Gravity pulled the swirling gas and dust together and resulted in the brightest star of the constellation of Lyre, Vega.
Fun Kids Facts For Haumea the Dwarf Planet
- Our Solar System is moving in Vega's direction at a speed of 24.1 km / 15 mi per second. This will make Vega appear brighter and brighter, and in about 210,000 years, Vega will become the brighter star in the night sky.
- Vega will remain the brightest star in the sky for another 270,000 years after this event.
- The Lyrid meteor shower is associated with Vega. It peaks every April of every year.
- Vega was the first star to have a car named after it.
- For the Romans, when Vega set below the horizon, it signaled the start of autumn.
- Vega is associated with Vanant, a minor divinity whose name means conqueror.
- Vega is among the first stars to have its distance estimated.
Size and Comparison
Vega has around 2.135 solar masses and 2.362 solar radii. It is almost five times bigger than our Sun and more than twice as massive.
Trivia
What Does Vega Star Mean?
The name of the star Vega comes from the Arabic word "waqi". This word translates to "falling" or "swooping". Vega was named as such since the constellation where it resides, Lyre, was associated with a swopping vulture rather than a lyre.
Is Vega the North Star?
Vega is not the north star; that would be Polaris. Vega was the north pole star in the year 12,000 BC. In the year 13,727, Vega will once again be the northern pole star.

What is the Vega Star Made of?
Vega is a blue main-sequence star made out of hydrogen and helium. It is currently fusing hydrogen into helium at its core. This process will continue for around 500 million years.
Vega Star Notes
- Vega is a blue main-sequence star of spectral type A0V.
- Vega is the fifth-brightest star in the night sky, and it is the brightest star in Lyra's northern constellation.
- Vega is a singular star, and it doesn't have any planets.
- Vega was our northern pole star in the year 12,000 BC. In the year 13,727, Vega will once again be the northern pole star.
- Our Solar System is moving in Vega's direction at a speed of 24.1 km / 15 mi per second. This will make Vega appear brighter and brighter, and in about 210,000 years, Vega will become the brighter star in the night sky.
- Because of this tremendous rotational speed, Vega is bulged at the equator. A circumstellar disk of dust surrounds this star.
- Many stars that have an infrared excess because of dust emission are termed Vega-like stars.
- Vega was the first star to be photographed, and it is also the first to have its spectrum recorded. Vega was photographed as early as 1850.
Sources:
Image Sources:
- https://miro.medium.com/max/5120/1*I3D-Y8yMScEImd7Ja_ofzw.jpeg
- https://www.upr.org/sites/upr/files/201906/vegaPS2-5900ea9b5f9b581d5902486e.png
- https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/proxy/RVKtY1P2Y1rFgRVenB5--5Oanpa7OyphRDqr9sVvw3zpmOaFmu82j_UKpj5ezGDSur8faXZ7z4ynBMhoF5YZBbGui1oP4S4zxaW6S4z8VWJjj_5WVwzsofsa492-om8WQQ-AU9b6JHUHHi3pT_ZTv_xD3KOzpoQ
- https://www.solarsystemquick.com/universe/vega-disc-5.jpg
