The Universe is considered by some to be infinite, while others find comfort in the fact that it may have an end. Throughout the ages of space exploration, the only certain thing is maybe the fact that the Universe will never be charted.
Why is this? It’s because of the endless galaxies that seem to pop out left and right, their sizes, distances, and other aspects. So how many galaxies are there in the Universe? Currently, the observable Universe, which has a radius of 46.5 billion light-years, seems to contain at least two trillion galaxies.
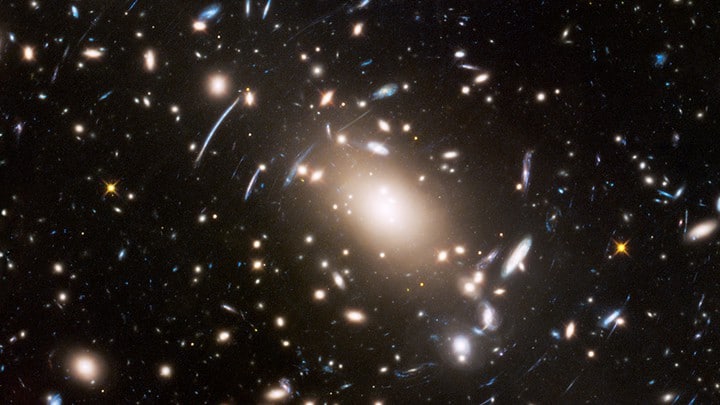

Our galaxy, the Milky Way, is just one among these numerous galaxies, and it isn’t even considered a big galaxy. It stretches for 105,700 light-years in diameter and may contain at least 100 billion planets and around 400 billion stars.
Now, if we were to imagine how many planets and stars those 2 trillion galaxies might have, we would probably have to throw out our calculators. This is especially true since some galaxies are several times larger than our Milky Way Galaxy.
Largest Galaxy Ever Discovered
The largest galaxy ever discovered in our Universe is the supergiant elliptical galaxy designated as IC 1101. This galaxy contains well above 100 trillion stars, and it stretches for over 5.5 million light-years across.
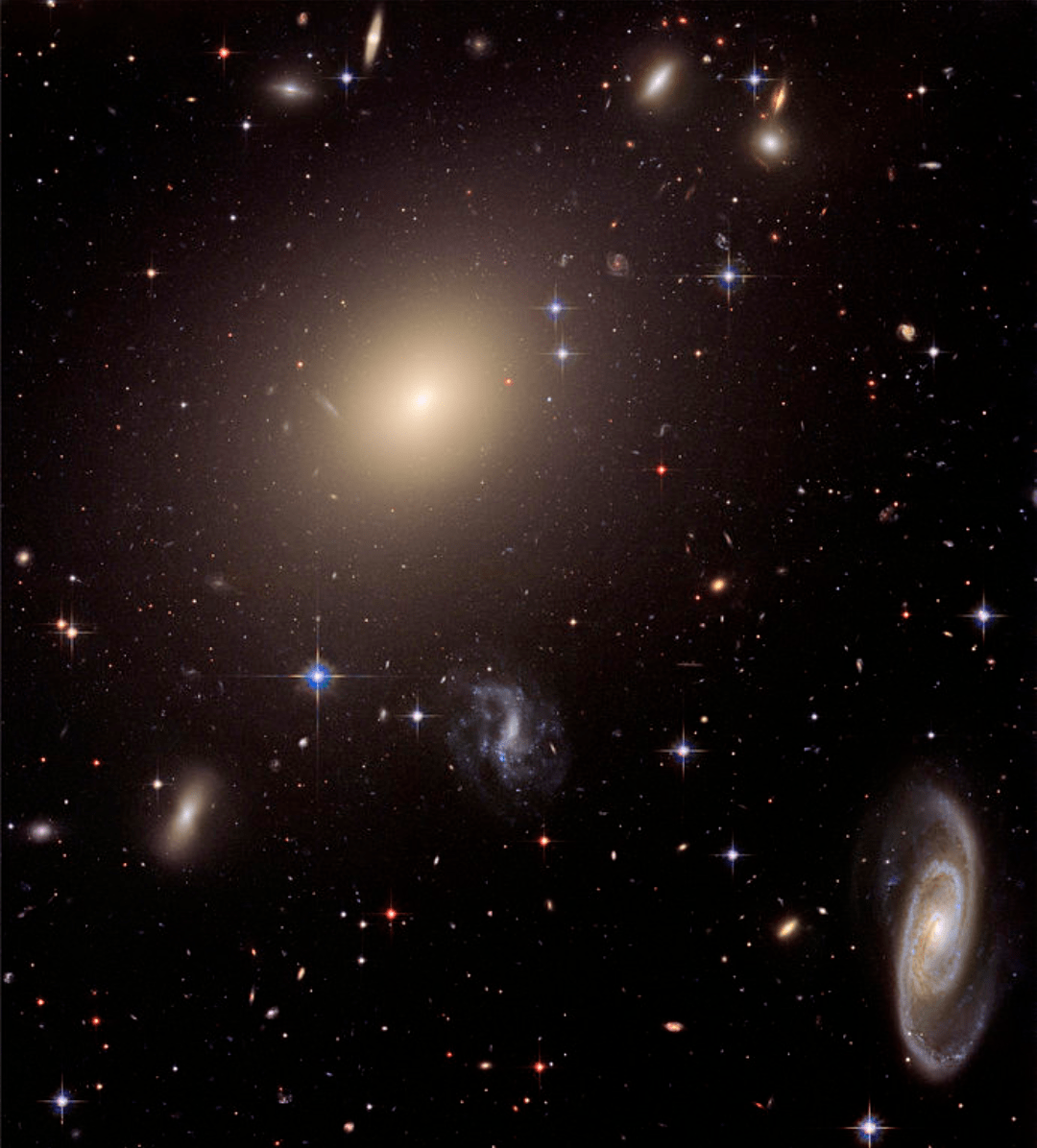
IC 1101 is around 50 times larger than our Milky Way Galaxy, and it is situated at approximately 1 billion light-years / 320 megaparsecs away from us.
How Many Galaxies are there in the Milky Way?
Our own Milky Way has some satellite galaxies, which are very small galaxies that are gravitationally bound to larger ones. These small galaxies have been or are in the process of being integrated/devoured by their larger brethren.

The Milky Way galaxy has satellite galaxies such as the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds. There are around fifty galaxies in the Milky Way, the largest of which is the Large Magellanic Cloud. This satellite galaxy has a diameter of only 14,000 light-years.
The Large Magellanic Cloud may have as many as 10 billion stars within it. This small galaxy will collide with our Milky Way in around 2.4 billion years.
How Many Galaxies are there in the Universe 2020?
Currently, in 2020, it was estimated that there are around 2 trillion galaxies in the observable Universe. Each galaxy is unique, ranging in size from 10,000 light-years to hundreds of light-years.
Galaxies have been classified under five categories: spiral, barred spiral, lenticular, elliptical, and irregular. Our Milky Way galaxy is a barred spiral galaxy.
Is the Milky Way a Large Galaxy?
The Milky Way is considered an average-sized galaxy. It stretches for 105,700 light-years in diameter and may contain at least 100 billion planets and around 400 billion stars.
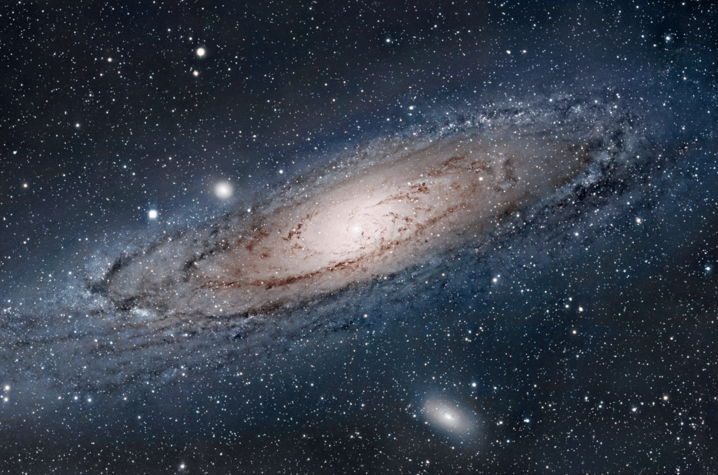

Now, if the Milky Way is an average galaxy, how does a giant galaxy look like? Well, it would like IC 1101, which is currently the largest galaxy ever discovered.
IC 1101 is more than 50 times larger than the Milky Way. It stretches for over 5.5 million light-years across. This galaxy may have trillions of stars and planets.
Can Humans Travel to Another Galaxy?
Humans could travel to other galaxies, but the technology involved would look very different from what we currently have. Galaxies are thousands or even millions of light-years away from one another; the distance is almost unfathomable.
The required technology for intergalactic travel is far beyond our current capabilities. They are mostly on the subject of speculation, hypothesis, or science fiction.
Reaching the speed of light is crucial for intergalactic space travel, and this presents its own problems and limits. Even if we were to travel at the speed of light, it would still take us thousands of years, in the best case, to reach another galaxy.

Take, for example, the Large Magellanic Cloud, which is one of the closest galaxies to our Milky Way. This small and minor galaxy is located at around 158,200 light-years away from us.
Thus, it would take you 158,200 years to reach it, and this implies traveling at the speed of light constantly, which also creates many problems.
We would need an endless amount of energy to do so, and we’ve not even begun to talk about food or water resources. As we can see, water is quite hard to find on other celestial objects.
Where would we get water on such trips? And heck, water is easy to find compared to food. Where would we find food while traveling to other galaxies?
As you can see, there are so many problems when it comes to intergalactic travel that it may seem impossible; however, we might one day make it possible.

There may be far better options for humanity to travel in space then just with the speed of light. If these options remain only purely hypothetical, such as the much-coveted wormholes, then we are indeed trapped within our own galaxy.
Another aspect we should take into consideration is the fact that galaxies move around, just like planets, and stars do. It has been proven that many galaxies are getting further and further away from us.
If we would want to reach other galaxies, our best chance is to go straight towards a galaxy which is coming our way, like the Andromeda Galaxy, for example.
The Andromeda Galaxy is on a collision course with our Milky Way Galaxy; however, this will happen in around 4.5 billion years from now. This number is far too great to help us in our intergalactic space travel endeavor.
How Many Universes Are There?
Since the Universe is so vast and complex, one might assume that other Universes exist. There is only one Universe we currently know of, and that is the Universe in which we already live.

The existence of other Universes certainly seems possible; however, we are still on the process of studying our own before hunting for others.
We know too little about our own Universe, and deciphering it is the key to finding out if there are other Universes out there.
Did you Know?
- Our Sun takes around 250 million years to orbit the Milky Way galaxy. This means that the Sun, already made about 20 orbits around the galaxy since it was born.
- We all orbit around a black hole, the one in the galactic center of the Milky Way, designated as Sagittarius A*.
- It is believed that the Milky Way galaxy has around two rogue planets for every star. They are planets that have been thrown out of their solar system. This can happen through collisions, or if their Sun underwent a stellar evolution and lost its grip on them.
- The outermost regions of the Milky Way suggest that it hasn’t undergone any mergers with large galaxies in the last 10 billion years.
- The Sombrero Galaxy is among the most massive objects located in the Virgo Cluster of galaxies. It has around 100 billion stars, and it is located at approximately 31.1 million light-years / 9.55 megaparsecs away from our Solar System. This galaxy has a diameter of roughly 49,000 light-years, which is 30% of the size of our Milky Way Galaxy.
- Galaxies such as the Sombrero Galaxy demonstrate that a galaxy’s size might not necessarily yield a greater or lesser number in stars.
Sources:
Image Sources:
- https://cdn.theatlantic.com/thumbor/eH8NqASddJOhPu1uzuCBLo35dTU=/0x320:1072×923/720×405/media/img/mt/2016/10/hs_2016_28_a_large_web/original.jpg
- https://thevoidabovenet.files.wordpress.com/2018/09/screenshot_20180912-204939.png?w=1080
- https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/3c/Eso1021d.jpg/1247px-Eso1021d.jpg
- https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/81/07-Laniakea_%28LofE07240%29.png/1200px-07-Laniakea_%28LofE07240%29.png
- https://scx1.b-cdn.net/csz/news/800/2017/evidenceofim.png
- https://images.theconversation.com/files/69707/original/image-20150122-29832-17j22fj.jpg?ixlib=rb-1.1.0&q=45&auto=format&w=926&fit=clip
- https://www.parhlo.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/09-1.jpg
- https://media3.s-nbcnews.com/j/newscms/2017_24/2035056/170612-multiverse-mn-1515_266eac1decce12ae64fed27574746675.fit-2000w.jpg
