A solar eclipse is an event in which a portion of the Earth is engulfed in a shadow cast by the Moon which fully or partially blocks sunlight. It occurs when the Sun, Moon, and Earth are aligned.
Key Facts & Summary
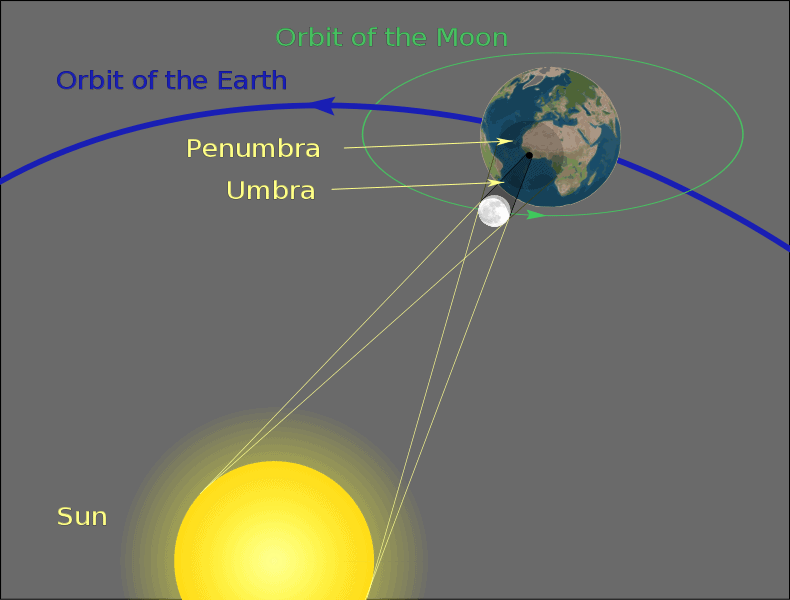
- The shadow created on the Earth by the moon during a solar eclipse is broken down into three parts. These are the umbra, penumbra and antumbra. The Umbra is the darkest part of the shadow, where the moon is completely covering the sun. The antumbra is the area surrounding this, where the moon is in front of the Sun but isn’t covering it in its entirety, so the shadow is not as dark. The penumbra is the outer area of the shadow where the moon is only covering a part of the Sun.
- A total eclipse is where the moon completely blocks out the sun. To observe this, you will need to be located in the middle of the shadow cast by the moon (the umbra). The total eclipse makes the sky very dark as though it is night time. This is the only type of eclipse that is safe to look at with the naked eye. All other types require sunglasses with a solar filter to prevent damage to the eye from the Sun’s rays.
- An annular eclipse is when the moon is in front of the Sun but is not blocking it out entirely, so a ring of light appears around its edges.
- This is usually because the moon is further away from the Earth in its orbit making the moon seem smaller.
- A partial eclipse is when the moon is not blocking out all of the Sun. This is because they are not quite lined up properly. When this is the case, you may see anything from a sliver of a shadow on the Sun to almost a total eclipse. It mostly depends on your location on
- Earth and which part of the shadow cast by the moon you are in.
- There are usually between 2 and 5 eclipses in any given year. It all depends on the geometry of the Sun, Moon, and Earth.
- Total solar eclipses happen on average one and a half years. The rarest solar eclipse is the total solar eclipse.
- The longest total solar eclipse lasts around seven and a half minutes.
- Almost identical solar eclipses happen every 18 years and 11 months. This period of 223 synodic months is called a saros.
- The word eclipse was used to describe this event as it is the Greek word meaning abandonment or downfall.
- During a total solar eclipse, air temperatures drop and sometimes gravitational paradoxes also occur.
- Planets appear as points of light during solar eclipses.
- Usually, the alignments of the Sun, Moon, and Earth coincide during a new moon – syzygy.
- In a total eclipse, the disk of the Sun is fully obscured by the Moon while in partial and annular eclipses only part of the Sun is obscured.
- In some ancient and modern cultures, solar eclipses were attributed to supernatural causes or regarded as bad omens.
- The word eclipse was used to describe this event as it is the Greek word meaning abandonment or downfall.
- There are 4 types of solar eclipses: total eclipse, annular eclipse, partial eclipse, and hybrid eclipse.
- Total solar eclipses cannot be seen from the North and South Poles. Only a partial solar eclipse is able to be viewed from those locations.
- The total solar eclipse, when the Moon completely obscures the Sun and leaves only the faint solar corona, is known as a Totality – 269 km/167 mi is the maximum width of the path of totality and it can sweep across an area of Earth’s surface about 10,000 mi / 16.093 km long.
- The speed of the Moon as it moves across the Sun is about 2.250 km / 1.398 miles per hour.
- Looking at a total solar eclipse without protection can permanently damage the eyes.
Solar eclipses are one of the most beautiful natural phenomena that can occur on Earth. In ancient times these events were both frightful, and spiritual in nature.

Thus solar eclipses have been noted since at least 763 BC. One of the earliest claims still-unproven is that of the archeologist Bruce Masse, who linked an eclipse that occurred on May 10, 2087 BC with a possible meteor impact in the Indian Ocean.
The Greek historian Herodotus wrote that Thales of Miletus predicted an eclipse that occurred during a battle between the Medes and the Lydians. Both opposing forces put down their weapons and declared peace due to the eclipse.
Chinese records of eclipses begin as early as 720 BC. However, the first telescopic observation of an eclipse was made in France in 1706. In 1715, the English astronomer Edmund Halley correctly predicted and observed the solar eclipse of May 3, 1715.
Later, in the mid-19th century, scientific understanding of the Sun was improving through observations of the Sun’s corona during solar eclipses.
Generally, the only solar eclipse that can damage the eyes is the total solar eclipse. Because our eyes adjust to the darkness and thus our pupils dilate and are striving to let light in as much as they can, a sort of shock can be produced if the Sun “surprises” you. This can cause permanent eye damage.
Types of Solar Eclipses

For a long period of time, only 3 types of solar eclipses were classified. However, a fourth one has now been established.
Total Eclipse
The most dangerous eclipse for the unprotected eye is the total eclipse. When the Moon completely blocks the solar disk, observers see a darkened Sun with a ghostly glow of the solar corona extending out to space. You can directly look at the Sun without protection, however, if the Sun catches you by surprise it can lead to permanent eye damage.
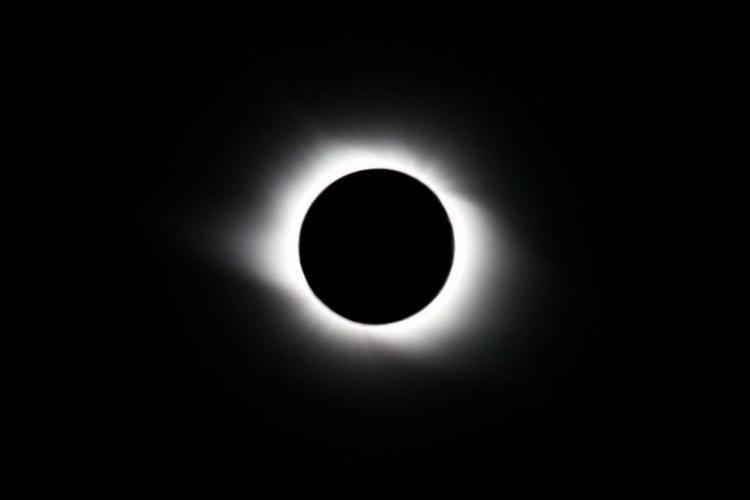

This type of eclipse hasn’t always been visible from Earth. In ancient times, the Moon was too close to Earth and during eclipses, it completely blotted the Sun’s disk. Sometimes, when the Sun is active, observers can see solar prominences, loops, and flares during totality. This eclipse can last at a maximum of about 7 minutes and 30 seconds.
Annular Eclipse
Similar to the total eclipse, the annular eclipse occurs when the Moon is farther away in its orbit than usual. Thus it is too “small” to completely cover the Sun’s disk. In this type of eclipse, a bright ring of sunlight shines around the Moon.
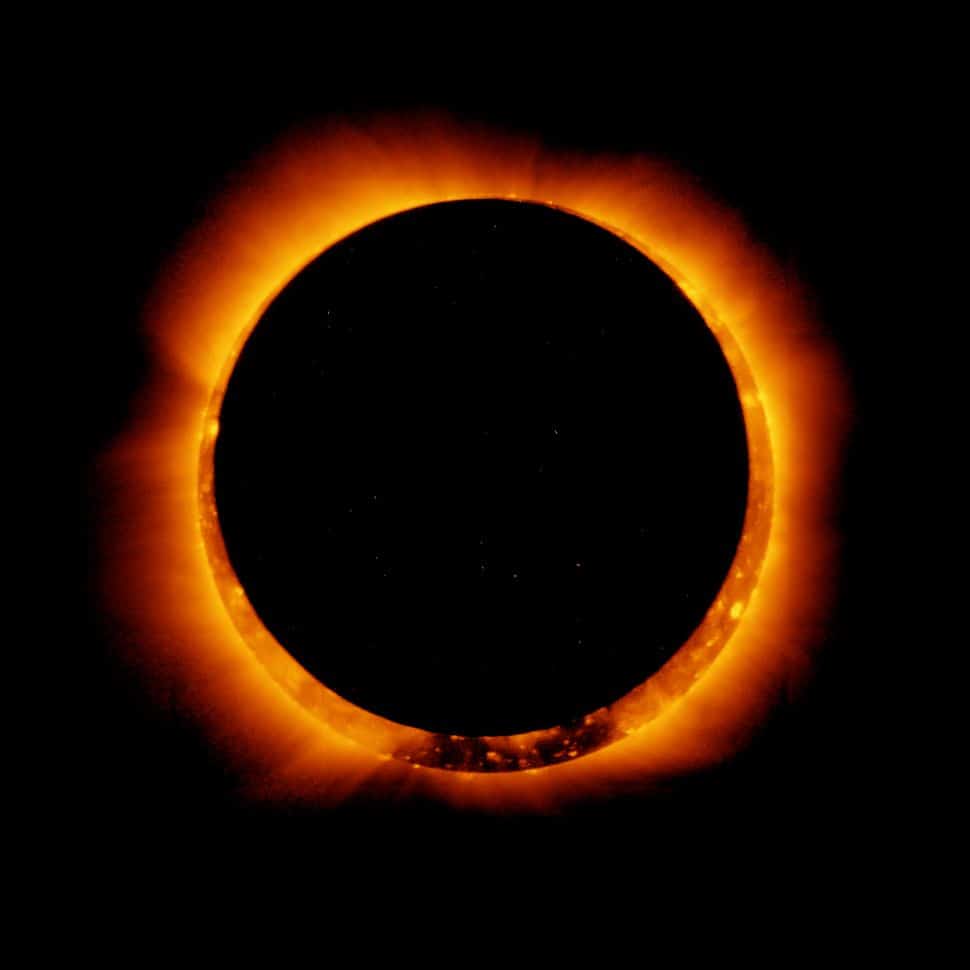

It is called annular because it comes from the Latin word “annulus” which means ring. This type of eclipse can last from 5 to 12 minutes. Again, protection is strongly advised if a person wants to look directly at it.
Hybrid Eclipse
The hybrid eclipse usually shifts between a total and an annular eclipse. At certain points on the surface of Earth, it appears as a total eclipse, whereas at other points it appears as annular. They are very rare in nature.
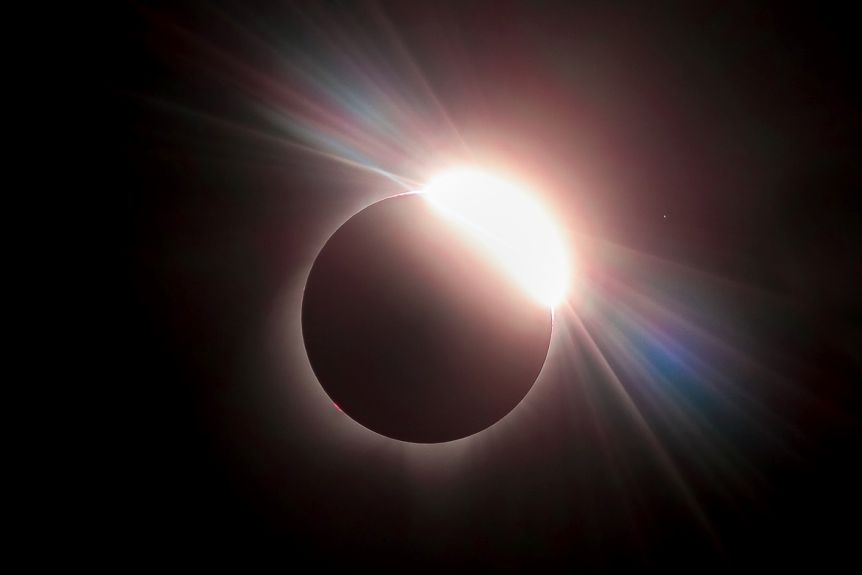

Partial Eclipse
Partial eclipses are quite common. They happen when the Moon partially obscures the Sun.
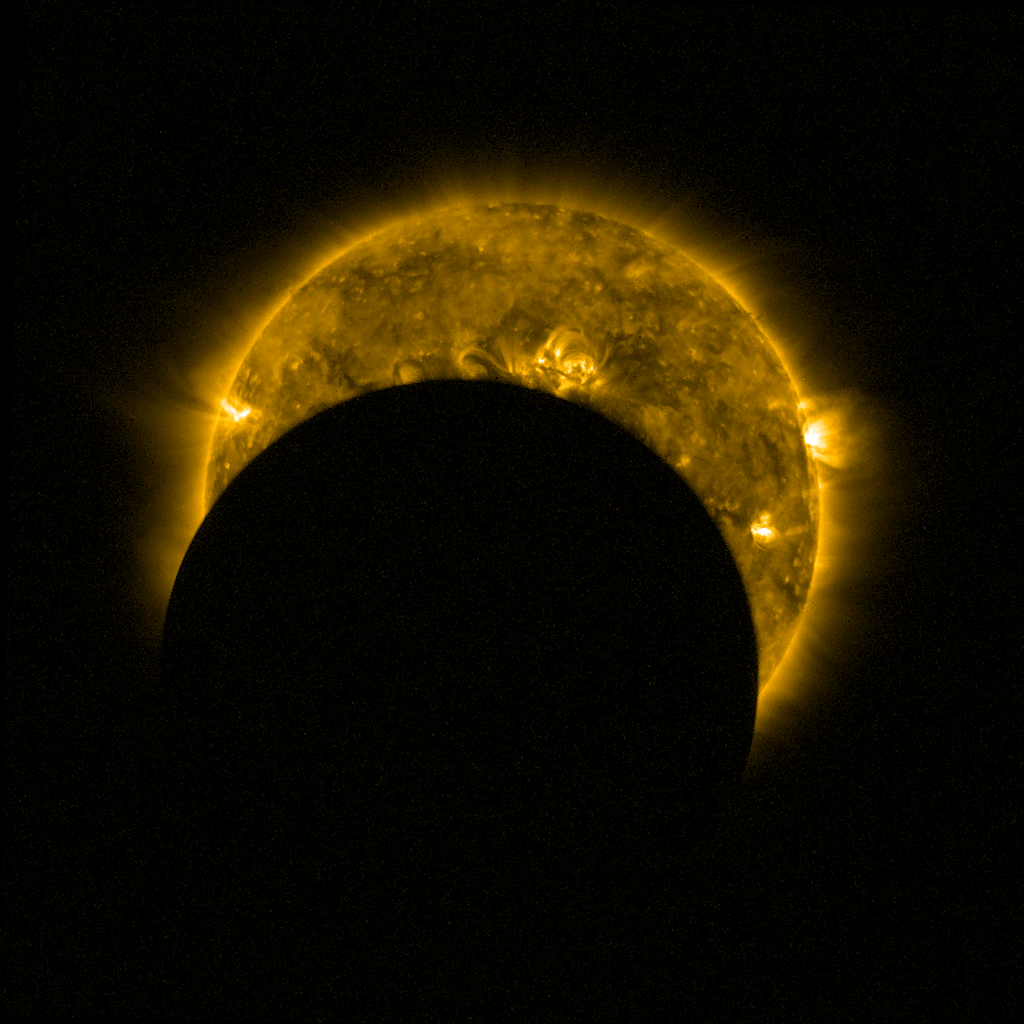
If the three celestial bodies do not form a straight line in space, a partial eclipse is produced. When that happens, a small part of the Moon’s surface is covered by the darkest, central part of the Earth’s shadow, called the umbra
Duration
There are 5 factors which determine the duration of a total solar eclipse:
1. The midpoint of the eclipse is near the subpolar point – which is “closest” to the Sun.
2. The vector of the eclipse path at the midpoint of the eclipse aligning with the vector of the Earth’s rotation.
3. The midpoint of the eclipse being very close to the Earth’s equator, where the rotational velocity is greatest.
4. The Earth is very near aphelion – its furthest point from the Sun in its elliptical orbit.
5. The Moon being almost exactly at perigee – making its angular diameter as large as possible.
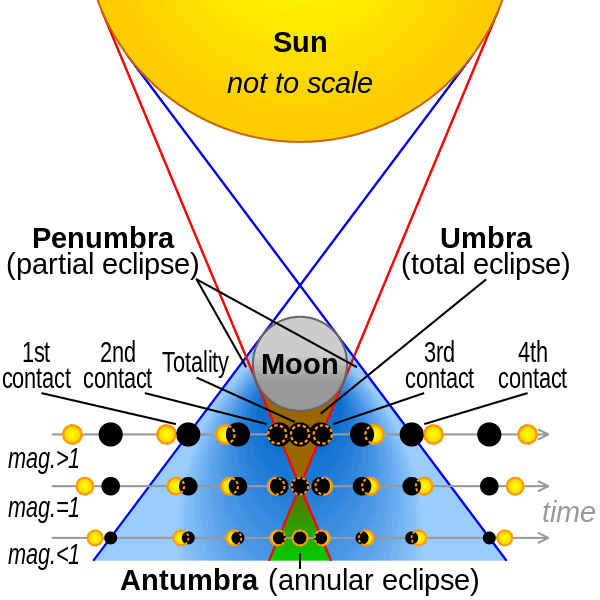
The shadow created on the Earth by the moon during a solar eclipse is broken down into three parts. These are the umbra, penumbra, and antumbra. The Umbra is the darkest part of the shadow, where the moon is completely covering the sun.
The antumbra is the area surrounding this, where the moon is in front of the Sun but isn’t covering it in its entirety, so the shadow is not as dark. The penumbra is the outer area of the shadow where the moon is only covering a part of the Sun.
Occurrence and Frequency
Total solar eclipses are rare events. They occur around 18 months on average, with reoccurrences at any given place only once every 360 to 410 years, on average. Between 2 to 5 solar eclipses occur every year, with at least one per eclipse season. On average, there are about 240 solar eclipses each century. There are many dedicated websites that track solar eclipses in order to help enthusiasts prepare to see them.
Anomalies
Many anomalies seem to occur during solar eclipses, especially ones related to gravity during the period of totality. Unexplained movements were reported by the physicist Maurice Allais, a phenomenon later named the Allais effect.
It remains controversial to this day. In 1970, the physicists Saxl and Allen observed the sudden change in the motion of a torsion pendulum. This phenomenon is called the Saxl effect.
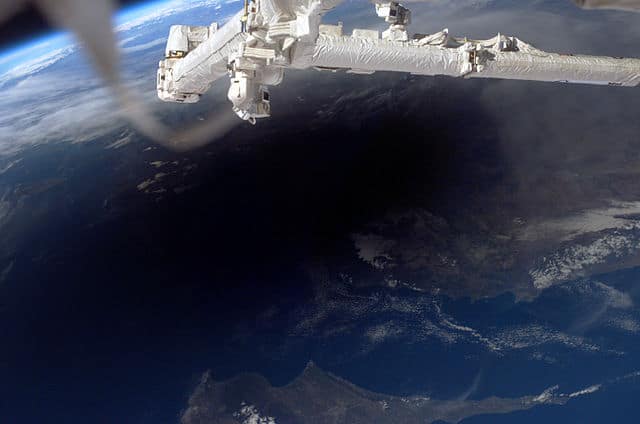

The solar eclipse that occurred on March 20, 2015, was the first to potentially have a significant impact on the power system.
The production of power decreased, as well as temperatures and wind power. Animals also changed their behavior, some returned to their nests and crickets chirp.
Did you know?
- If the Moon were in a perfectly circular orbit, a little closer to the Earth, and in the same orbital plane, there would be total solar eclipses every new moon.
- Hundreds of millions of years in the past, the Moon was closer to the Earth and therefore apparently larger, so every solar eclipse was total or partial, and there were no annular eclipses.
- Millions of years in the future, the Moon will be too far away to fully occlude the Sun, and no total eclipses will occur.
- Due to tidal acceleration, the orbit of the Moon around the Earth becomes approximately 3.8 cm more distant each year.
- The Chinese King Zhong Kang supposedly beheaded two astronomers, Hsi and Ho, who failed to predict an eclipse 4,000 years ago.
- The first photograph of a total eclipse was taken on July 28, 1851.
- The Earth continues to receive at least 92 percent of the amount of sunlight it receives without an eclipse
- In principle, the simultaneous occurrence of a solar eclipse and a transit of a planet are possible. But these events are extremely rare because of their short durations.
- The next total eclipse will occur in 2024, on the 8th of April. It will occur in North America.
- Other planets from the solar system experience solar eclipses as well.
- A triple eclipse happens on Jupiter once or twice every 10 years. They are produced by the Io, Callisto, and Ganymede moons.
- Only one side of both Pluto and its moon Charon will ever experience eclipses.
Sources:
Image source:
- https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/ae/Exit_Diamond_Ring_Effect.jpg/476px-Exit_Diamond_Ring_Effect.jpg
- https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/00/Geometry_of_a_Total_Solar_Eclipse.svg/790px-Geometry_of_a_Total_Solar_Eclipse.svg.png
- https://c.tadst.com/gfx/750×500/total-solar-eclipse.jpg?1
- https://cdn.mos.cms.futurecdn.net/JPzwHvtUp6n7gvPDoPkung-970-80.jpg
- https://www.abc.net.au/cm/rimage/11143234-3×2-xlarge.jpg?v=2
- https://www.esa.int/var/esa/storage/images/esa_multimedia/images/2017/03/proba-2_partial_eclipse_26_february_2017/16835822-1-eng-GB/Proba-2_partial_eclipse_26_February_2017_pillars.png
- https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/ad/Solar_eclipse_visualisation.svg/600px-Solar_eclipse_visualisation.svg.png
- https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/42/Eclipse_fromISS_2006-03-29.jpg/640px-Eclipse_fromISS_2006-03-29.jpg
