Distances in our solar system are mind boggling especially when we consider that the circumference of our own planet is 24,901 miles. We see that as massive but compared to the sizes of other planets and their distances from us this is miniscule.
What Is the Sun?
The orb that is visible in our daylight sky which we know as the sun is in fact a star. This star is classified as a yellow dwarf and is central to our solar system. Earth and the other planets of our solar system orbit this vast star. In fact it is our own planet’s rotation and orbit which creates the appearance of the sun moving across our sky. It itself is stationary as we revolve around it.
How Big Is the Sun?
The sun on a clear day is visible from the earth and in fact we should never stare directly at it. This is despite it being 93 million miles away so just how big is this giant orange orb? Scientists estimate that the sun has a radius of roughly 435,000 miles.
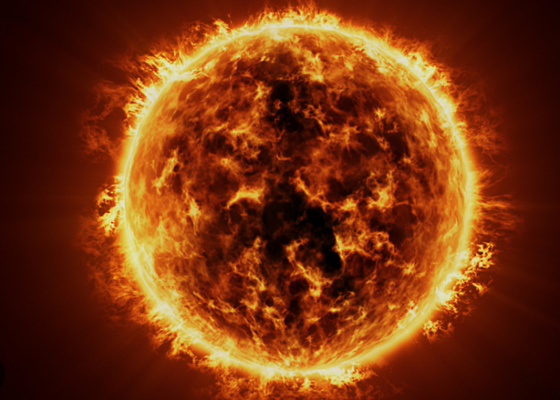

This may sound massive but there are many known stars which are much larger. In comparison to our planet however the son is roughly 330,000 times the mass of earth and we could fit our planet into the sun 1.3 million times.
What Holds the Sun Together?
The sun because it is a star is actually a huge ball of gas which is held together by its own internal gravitational forces. It is made up of several regions which include in order from the center out:
- Core
- Radioactive zone
- Convection zone
- Photosphere
- Chromosphere
- Transition zone
- Corona
Once material exits the corona of the sun at supersonic speeds, it becomes what is known as a solar wind. This solar wind forms a huge magnetic bubble of sorts around the sun which is known as the heliosphere. It is this heliosphere that extends beyond the orbit of all the planets in our solar system. Essentially our planet as well as all others in the solar system are held within the sun’s atmosphere.
What Is Mars?
Mars is one of the four terrestrial planets in our solar system and is the fourth planet from the Sun. At 2,106 miles its radius is the second smallest in our solar system. It is a cold desert world that is dynamic featuring seasons, polar ice caps, canyons and extinct volcanoes.
It is one of the most explored bodies in the solar system and has seen rovers landed on its surface multiple times. In fact at present there are two rovers, one lander and one helicopter exploring the surface of this planet.
In theory the closest Earth and Mars can get is 33.9 million miles. This however has never been witnessed in recorded history. The closest ever recorded was 34.8 million miles in August of 2003. According to NASA the two planets will not be as close again until 2237.
Mars’ Structure
Mars is around half the diameter of Earth, and has a surface area which is only slightly less than Earth’s total dry land mass. It is also less dense than Earth, with about 15% of Earth’s volume and 11% of Earth’s mass. This results in it having about 38% of Earth’s surface gravity.
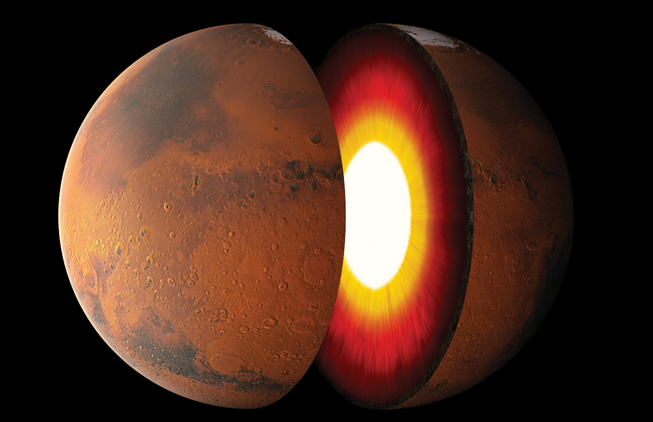
Mars has a red-orange appearance to its surface which is caused by ferric oxide, or rust. Its other common surface colors include golden, brown, tan, and greenish with color depending on the minerals present in those specific regions of the surface.
Internal Structure
Mars is similar to Earth in terms of its internal structure in that it has a dense metallic core which is overlaid by layers of far less dense materials. The core is estimated to be made of iron, nickel and sulfur. Around the core is a mantle that ranges between 770 – 1,170 miles in depth. The next layer, the crust, ranges from 6 – 60 miles in depth and includes iron, magnesium, aluminum, calcium and potassium.
The Surface
The various colors of the surface of Mars depend on the dominant minerals present in the various regions. Most commonly referred to as reddish in color though, this is due to rusting of iron within the surface rocks. Dust from these rocks gets kicked up into the atmosphere making the planet appear reddish.
Volcanoes, impacts from meteors, crustal movement and atmospheric conditions have combined to create the unique topological features of Mars. A notable feature of Mars’ surface is Valles Marineris, a large canyon that stretches roughly the distance from California to New York. To put that into perspective that is 10 times the size of the Grand Canyon on Earth.
Mars is also home to the largest volcano in the solar system. Known as Olympus Mons, it is three times as tall as Everest and its base covers roughly the same area as the state of New Mexico. There is also evidence on Mars of having had surface water several billion years ago.
Does Mars Have Moons and Rings?
Mars may be a small planet but it does have its own moons. These are Phobos and Deimos. It is thought that these two moons may have formerly been asteroids that were captured by Mars’s gravity. They are not spherical moons however as their mass is so low that gravity can not form them as such. Instead Phobos and Deimos are potato-shaped.
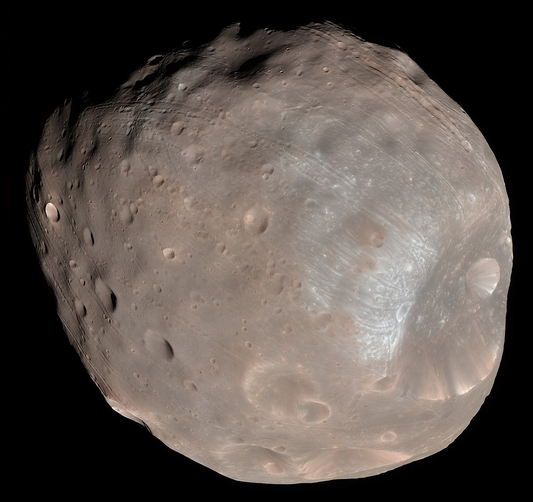

Currently Mars is not one of the planets in our solar system which has rings surrounding it but there is a chance that one day it will. This is because Phobos, the closest of Mars’s moons, is gradually being drawn toward the surface. It is estimated that in around 50 million years it will crash into mars and break apart. When this happens the resulting ejection of dust may form into rings around Mars.
History of the Observation of Mars
Earth is the third planet from the Sun meaning Mars as the fourth is actually a near neighbor to our own planet. So although Mars is a small planet it is easily visible in the night sky and has been noticed since ancient times.
The ancient Sumerians called it Nergal after their god of war and plague. Later the Mesopotamians referred to it as a star of judgment for the dead. It was noted as a wandering object in the night sky by ancient cultures which made it stand out from the stars.
Babylonian astronomers were able to make regular records of the positions of the visible planets and were able to determine that Mars made 42 circuits of the zodiac, every 79 years. From these observations they developed equations for making minor corrections to the predicted positions of the planets.
Mars Through a Telescope
If you knew where to look you could see Mars with the naked eye but with the advent of telescopes our understanding of Mars grew vastly. As with so many of the other planets it was astronomer Galileo Galilei who was first to view Mars through a telescope in 1610.

In the 19th century telescope resolution had become so advanced that they were sufficient to see details of Mars’s surface. It was Italian astronomer Giovanni Schiaparelli who used a 8.7 inch telescope to help produce the first detailed map of Mars.
Robotic Exploration
As one of our neighbors we have a reasonable ability to send probes to the surface of Mars especially because it, like Earth, has a solid surface. Countries such as the United States, Soviet Union, India, Europe, United Arab Emirates and China have sent dozens of unmanned spacecraft to Mars over the decades.
The first crewless spacecraft to visit Mars was Mariner 4, having been launched on November 28th 1964. It took just short of 8 months to reach the planet to take deep space images and readings of Mars from a close orbit.
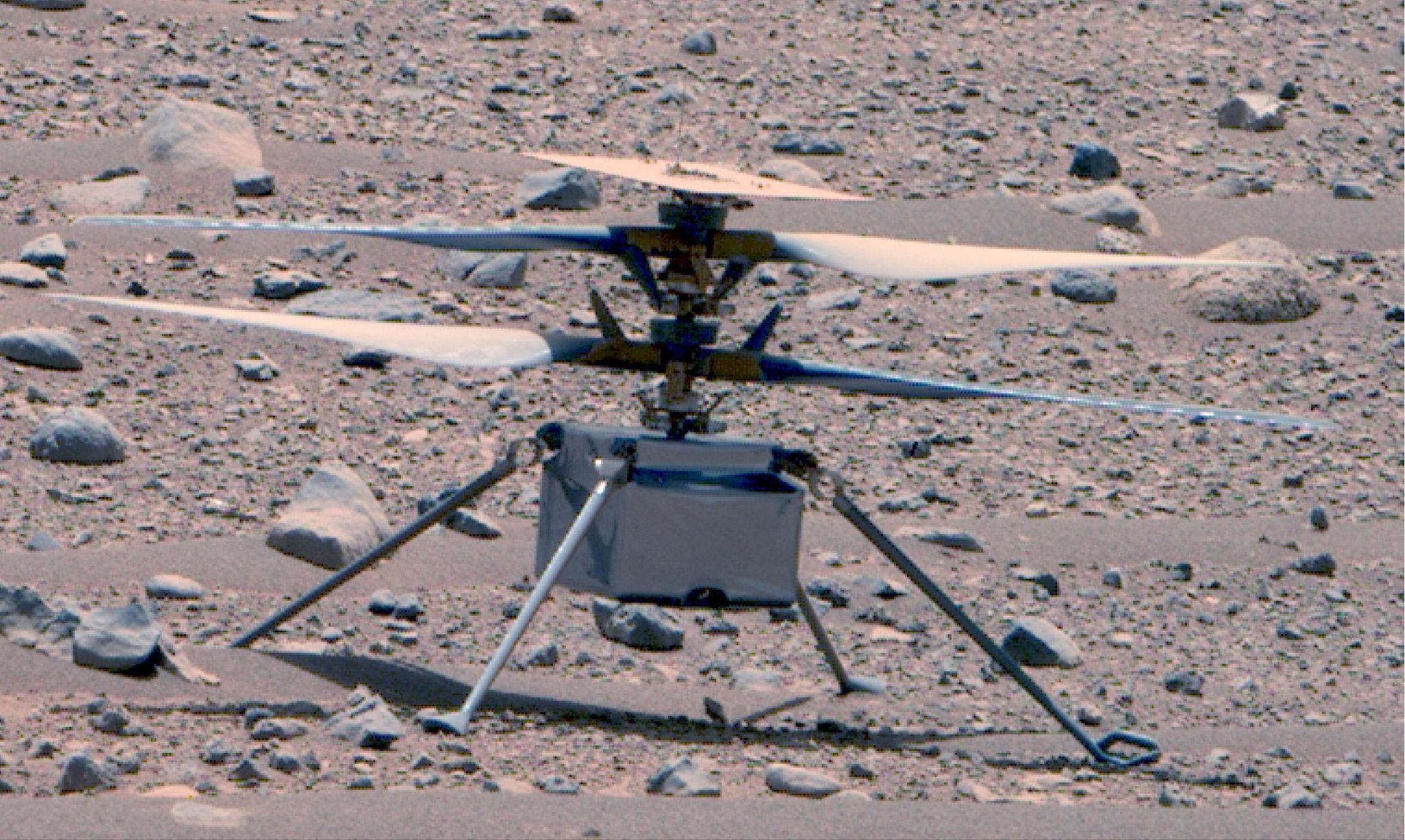
Subsequent trips and missions discovered more and more about the planet getting more detailed maps of the surface. Theories of potential life on Mars have been debunked by visits to the planet’s surface by several probes and rovers over the years.
As of 2023 there are five functioning spacecraft on the surface of Mars, these are:
- Mars Science Laboratory Curiosity rover
- Perseverance rover
- Ingenuity helicopter
- Tianwen-1 lander
- Zhurong rover
Circling Mars in orbit are:
- 2001 Mars Odyssey
- Mars Express
- Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter
- MAVEN
- ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter
- Hope orbiter
- Tianwen-1 orbiter.
There are further missions planned to reach Mars such as the Rosalind Franklin rover mission which should have launched in 2018 but is expected to finally take off at the earliest in 2024. There is also a proposed mission to launch in 2026 that would travel to Mars and return with surface samples.
How Far Is Mars From the Sun?
Mars is the last of the four terrestrial planets in our solar system in terms of distance from the Sun. It sits beyond Earth which is third closest. Its year lasts 687 Earth days which means this is how long it takes to complete a single orbit of the Sun.
Its orbit is not perfectly circular so at any given time during its orbit it can vary in terms of the distance that separates the two. On average it is 142 million miles (228 million kilometers) away from the Sun although it can be both closer and further away depending on its position in its orbit.
Final Thoughts
It takes about 13 minutes for light to reach Mars from the Sun. In contrast light reaches Earth in just over 8 minutes which should give you some idea of how much further away Mars is from the Sun as opposed to the distance between the Sun and Earth. At an average of 142 million miles from the Sun at any one time there is a vast distance between the two.
