We will learn more about Ceres in this post and some of the impressive statistics that surround this body in our solar system. So if you want to find out the answers to Ceres’s orbital period read on.

What Is Ceres?
Ceres is a dwarf planet found in the extensive asteroid belt that sits between Mars and Jupiter. It is a small dwarf planet that usually can not be seen with the naked eye from Earth unless the skies are especially dark.
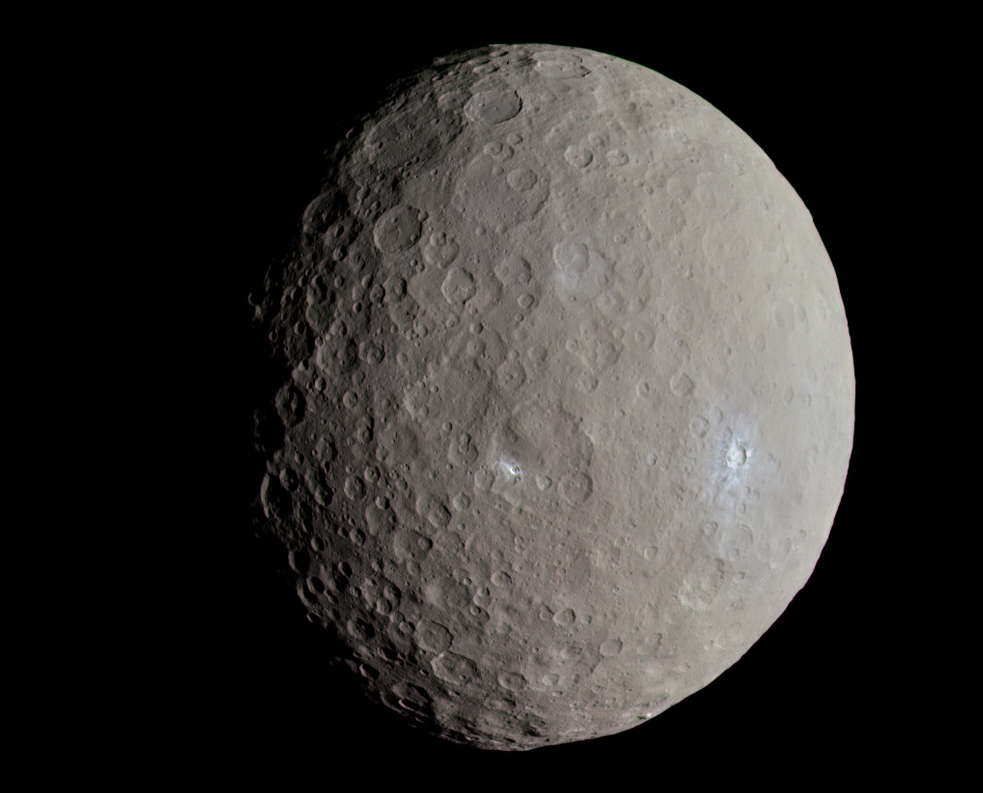

Although its presence has been known for over a century little was really known about it until 2015. It is the largest object within the asteroid belt and the only dwarf planet to be found within the inner solar system.
How Far is Ceres from Earth?
The smallest but closest to the Sun of all dwarf planets Ceres is far closer than the likes of Pluto and Eris. It is situated between Mars and Jupiter and its distance from the Earth varies based on the positions in our respective orbits.
Sometimes Earth and Ceres are closer to each other than to others. When at their closest Earth is roughly 146,309,842 miles away from Ceres. The two have not been that close since February 11th 1636.
How Far is Ceres from the Sun?
Eris is also 2.8 astronomical Units (AU) from the Sun with 1 AU being equal to the distance between Earth and the Sun. This equates to Ceres being roughly 257 million miles (413 million kilometers) away from the Sun on average.
Ceres’s Structure
Named for the Roman goddess of corn and harvests Ceres was likely formed 4.5 billion years ago when gravity pulled swirling gas and dust together to become this small dwarf planet. It is often referred to as an embryonic planet because it started to form but did not quite reach completion.
The reason it did not fully form is thought to be the gravitational effects of nearby Jupiter, a massive gas giant planet. Ceres likely settled into its current orbit among the asteroid belts leftover pieces about 4 billion years ago.
As a dwarf planet its structure is similar to that of the first 4 planets of our solar system Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. It is however not as dense although it does have layers like the four terrestrial planets. These layers are less clearly defined but it likely has a core and a mantle.
It is likely the planet is made up of roughly 25% water which means it would actually have more than Earth. The crust is most likely rocky and dusty with sizable salt deposits. This isn’t your average table salt however as there may be several types of salt based on different minerals for example magnesium sulfate.
Surface
Despite the fact Ceres must have been peppered by countless asteroids over the last 4 billion years, its surface craters are relatively small although numerous. It is likely that the effects of ice and low density surface materials such as salts may have smoothed Ceres somewhat. Ice volcanoes may also have covered large craters that once existed on Ceres’s surface.
Atmosphere
There is a very thin atmosphere on Ceres which seems to have water vapor. This has likely come from either ice volcanoes or surface ice sublimating. The nature of Ceres and its atmosphere has scientists interested in searching for signs of basic life. Unlike other planets of the solar system Ceres like Earth has surface water.
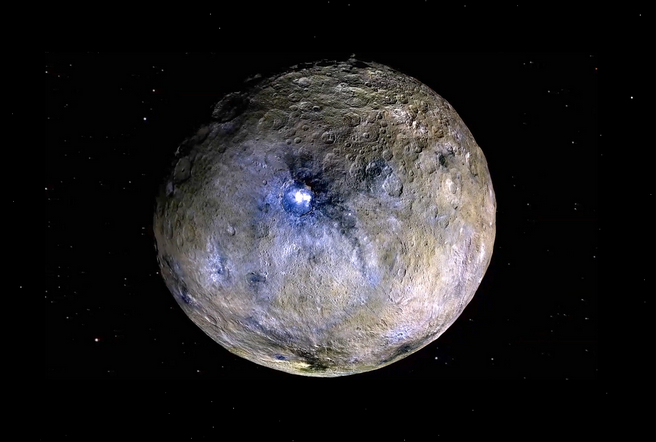

Does Ceres Have Moons and Rings?
Ceres does not have any moons orbiting it although it orbits alongside hundreds of asteroids within the belt. It also has no rings. It seems unlikely that moons or rings are in Ceres’s future.
History of the Observation of Ceres
Although technically visible with the naked eye from earth in perfect conditions the astronomers of antiquity had no knowledge of Ceres’s existence. As early as 1596 theoretical astronomer Johannes Kepler thought there may be another planet between Jupiter and Mars. This is due to evident gravitational effects on the two planets.
Essentially astronomers felt like another planet may be there somewhere but they could not locate it. In 1800, Franz Xaver von Zach, editor of the German astronomical journal Monatliche Correspondenz headed a group which sent requests to 24 experienced astronomers. These astronomers were dubbed the “celestial police,” and were asked to combine their efforts in the search for this potential planet. This resulted in the discovery of the asteroids Pallas, Vesta and Juno.
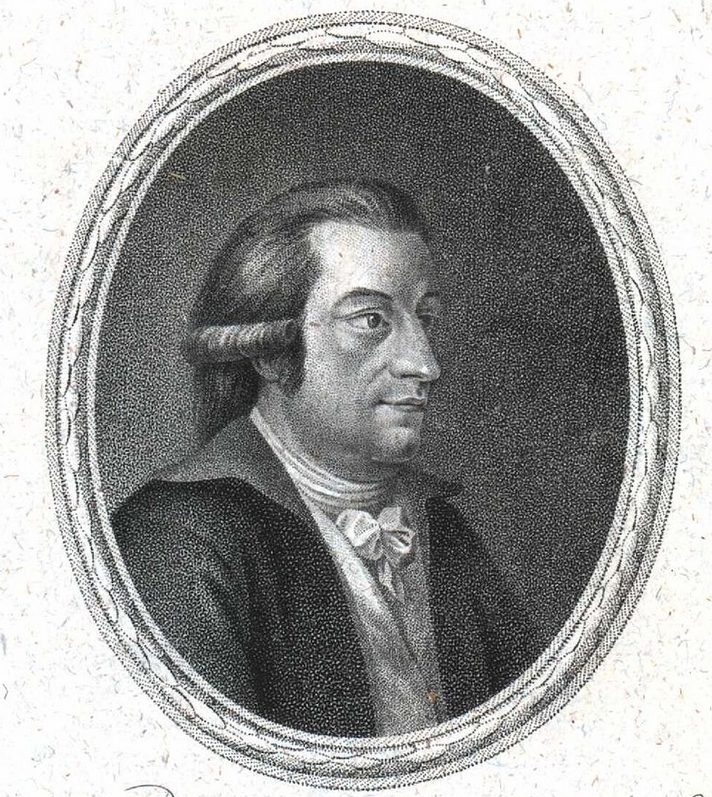

Among these 24 astronomers was Catholic priest Giuseppe Piazzi who attended the Academy of Sicily. On January 1st 1801 before being invited to the group Piazzi actually found Ceres. Searching for a specific star, Piazzi actually located a moving star-like object which he assumed to be a comet. He would view it 24 times between January 1st and February 11th 1801.
Ceres was lost track of briefly as Piazzi had to take a break due to illness and by the time his findings were reported to other astronomers it had moved too close to the Sun to be visible. It eventually moved away but not enough was known of its orbit to predict where it would next be seen.
It took mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss to develop an efficient method of orbit determination. It would take him a few weeks of work but he was able to predict where Ceres should be in the night sky. It was late December of 1801 that Ceres was relocated.
Initially thought to be a comet it quickly became assumed to be the missing planet but ultimately would be classified as a Dwarf Planet.
Space Exploration
The Dawn spacecraft was the first space to pass close to Ceres. It was launched on September 27th 2007 intending to make its first stop Vesta. On May 3rd 2011, the Dawn acquired its first images of Vesta and would proceed to orbit it for thirteen months. The Dawn then used its ion engine to depart for Ceres, being captured into the dwarf planet’s gravity on March 6th 2015.
There are talks of mounting future missions to try and find out more about Ceres and may even include attempts to gather mineral samples from the surface. China currently seems the most likely to embark on a future mission of exploration to Ceres.
What Is the Sun?
The orb that is visible in our daylight sky which we know as the sun is in fact a star. This star is classified as a yellow dwarf and is central to our solar system. Earth and the other planets of our solar system orbit this vast star. In fact it is our own planet’s rotation and orbit which creates the appearance of the sun moving across our sky. It itself is stationary as we revolve around it.
How Big Is the Sun?
The sun on a clear day is visible from the earth and in fact we should never stare directly at it. This is despite it being 93 million miles away so just how big is this giant orange orb? Scientists estimate that the sun has a radius of roughly 435,000 miles.
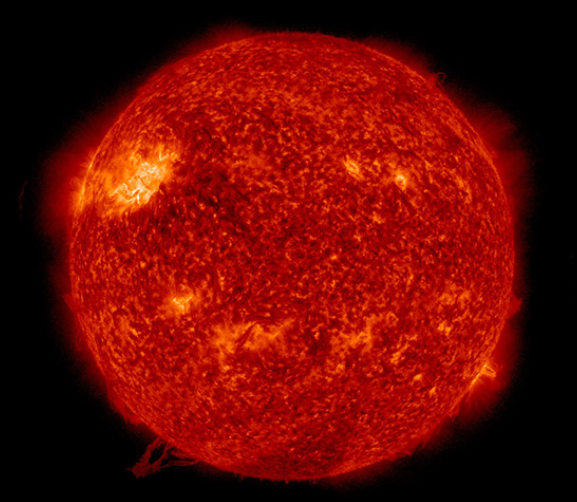
This may sound massive but there are many known stars which are much larger. In comparison to our planet however the son is roughly 330,000 times the mass of earth and we could fit our planet into the sun 1.3 million times.
What Holds the Sun Together?
The sun because it is a star is actually a huge ball of gas which is held together by its own internal gravitational forces. It is made up of several regions which include in order from the center out:
- Core
- Radioactive zone
- Convection zone
- Photosphere
- Chromosphere
- Transition zone
- Corona
Once material exits the corona of the sun at supersonic speeds, it becomes what is known as a solar wind. This solar wind forms a huge magnetic bubble of sorts around the sun which is known as the heliosphere. It is this heliosphere that extends beyond the orbit of all the planets in our solar system. Essentially our planet as well as all others in the solar system are held within the sun’s atmosphere.
How Long Does it Take Ceres to Go Around the Sun?
Ceres is the closest dwarf planet to the Sun by a long margin but it is still further from our star than we are on Earth. The further a body orbiting the Sun is from it the longer its orbital period lasts because it must travel further to complete a full orbit.
This small and rapidly spinning dwarf planet completes its day in 9 Earth hours with its extra distance from the Sun meaning a year on Ceres lasts 1,682 Earth days. This equates to an orbital period for Ceres of roughly 4.6 Earth years.
Final Thoughts
Despite the short days and extended length of a year on Ceres it does not experience seasons. This is because it spins at a 4 degree angle meaning it is almost completely upright. As a result surface conditions tend to remain consistent throughout the dwarf planet’s orbital period.
