Leo constellation is one of the youngest recognized constellations. It is also known as the "lion" constellation, and it is located in the northern celestial hemisphere. It is one of twelve zodiac constellations.
Key Facts & Summary
- Among the 88 modern constellations, Leo is the 12th largest constellation in the sky, and it extends approximately 947 square degrees across the sky.
- It is visible from both the Southern and Northern hemispheres.
- In Greek mythology, Nemean Lion would make women as his prisoners in his den so that warriors came and save them. He would ambush them.
- Leo has five Messier objects the galaxies Messier 65, Messier 66, Messier 95, Messier 96 and Messier 105.
- There is a tiny group of galaxies called the Leo Triplet, which consists of the galaxies: Messier 65, Messier 66, and NGC 3628
- Two meteor showers called the Leonids, and the January Leonids, are correlated with the Leo constellation.
- The most famous stars in the Leo constellation are Regulus, Denebola, and Wolf 359.
- Leo is part of the Zodiac family constellations, along with Aries, Taurus, Gemini, Cancer, Virgo, Libra, Scorpius, Sagittarius, Capricornus, Aquarius, and Pisces.
- The shiniest star in the Leo constellation is Regulus, which has a magnitude of 1.35. It can be seen with the naked eye.
- Leo's constellation has 13 named stars, which have been approved by the International Astronomical Union: Adhafera, Algieba, Alterf, Chertan, Denebola, Dingolay, Formosa, Moriah, Rasalas, Regulus, Sagarmatha, Subra, Zosma. These are also the brightest stars.
- Regulus with Spica and Arcturus form a well-known asterism called the Spring Triangle.
- Besides the Messier objects, we can also observe other fantastic celestial objects in the constellation of Leo, such as the Leo Ring, NGC 2903, the Clowes Campusano LQG, U1.11, and the Huge-LQG.
The Constellation of Leo for Kids
The constellation of Leo is among the largest zodiac constellations in the sky. It is full of deep-space objects and bright stars. Many Messier objects are present here as well.
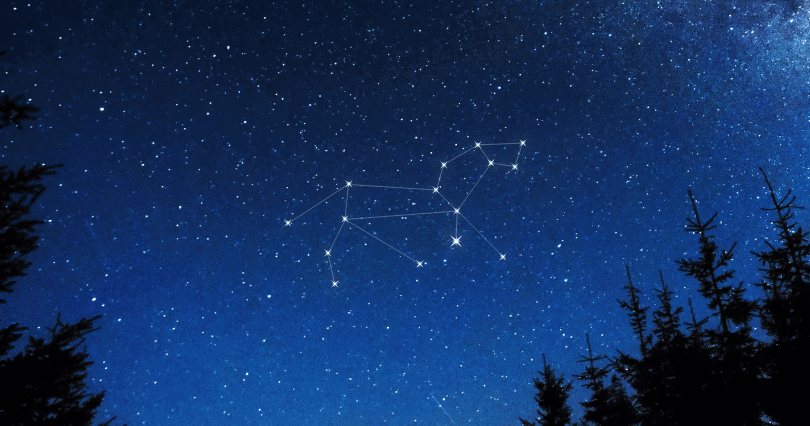

Some asterisms are present in the constellation of Leo as well. This constellation is quite ancient since evidence of its existence date back to as early as 4000 BCE. The Mesopotamians being the oldest ones to have a similar constellation to Leo recorded.
What Does the Constellation of Leo Represent?
The constellation of Leo represents a lion's head. In Greek mythology, the Nemean Lion took women as prisoners to lure warriors into his den. The Nemean Lion was defeated by the great hero Hercules, and he took its skin and wore it in further battles.

Where Can you See the Constellation of Leo?
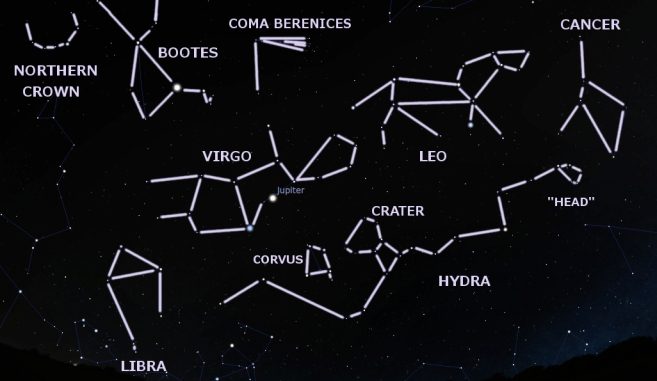
Leo's constellation spreads out for 947 square degrees and is located in the second quadrant of the northern hemisphere. It is most visible around the spring equinox, and it lies between the Cancer constellation to the west and Virgo to the east.
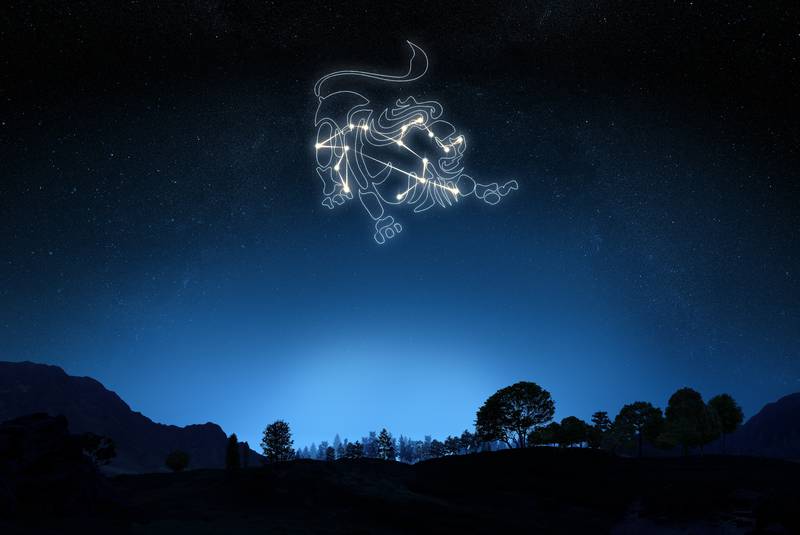

The constellation of Leo has the shape of a lion, and if you want to find it, you must first need to look for the Big Dipper in the northeast sky. Here you can see the two pointer stars from the Big Dipper. If you draw a line between these stars, it points towards the North Star, and the constellation of Leo.
What is the Best Season to See Leo Constellation?
The best season to see Leo Constellation is in the spring equinox. You can identify it in the Northern Hemisphere in May or April. This is when the constellation is the most prominent in the night sky.
When Can Leo be Seen in the Night Sky?
Leo Constellation can be seen from both hemispheres from January to June. It has many shiny stars, which makes it one of the most recognizable constellations in the night sky.
Fun Kids Facts About the Constellation of Leo
- The most shining star in the constellation of Leo is Regulus. It is also designated as Alpha Leonis. Regulus is a blue-white subgiant star.
- The Roman poet Ovid named the constellation Hercules Leo and Bacchi Sidus. Bacchus was a famous God in mythology, and he was associated with lions.
- In Greek Mythology, Leo was a lion who was defeated by Hercules during one of his twelve labors. After his death, Hercules put him up in the sky.
- Every year, a meteor shower takes place, which appears in the same line of sight as the constellation of Leo.
- There are a total of 156 stars located in Leo.
- It is believed that in Astrology, the Sun is in Leo from the 23rd of July to the 22nd of August.
- In the Harry Potter series, the well-known Sirius Black has a brother, Regulus, who is named after the brightest star in Leo.
- The Roman Poet Marcus Manilius named Leo "Jovis et Junois Sidus," which meant "Star of Jupiter and Juno."
- In Sumeria, Leo was pictured as the monster Humbaba, who was defeated by Gilgamesh.
- Leo has 22 stars, which have confirmed planets.
Size and Comparison
Leo Constellation occupies an area of 947 square degrees. It is the 12th biggest constellation in size, and it can be seen at latitudes between +90o and -65o. It is among the most prominent zodiac constellations.
Trivia
What is the Brightest Star in the Constellation of Leo?
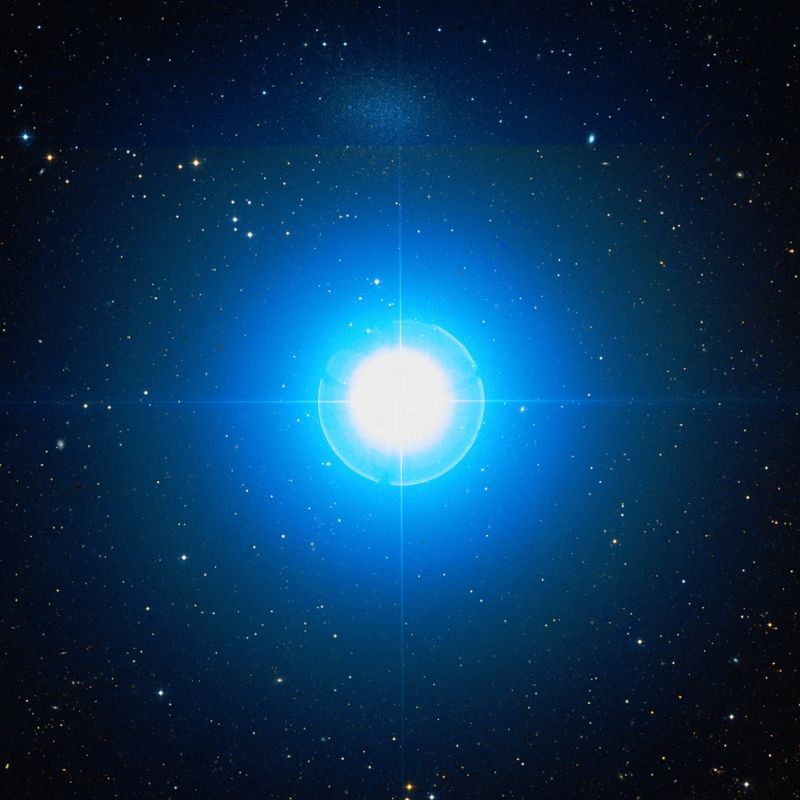
Regulus / Alpha Leonis is the brightest star in Leo Constellation and also the 21st brightest star in the night sky. It is made out of four stars, which are grouped into two pairs. This cool blue-colored star is located at the base of the most outstanding asterism in Leo, called The Sickle of Leo. The sickle of Leo has many stars that outline the mane of the Lion.
How Many Messier Objects are in the Constellation of Leo?
Leo Constellation has five Messier objects, the galaxies Messier 65, Messier 66, Messier 95, Messier 96, and Messier 105. All of them are very bright galaxies.
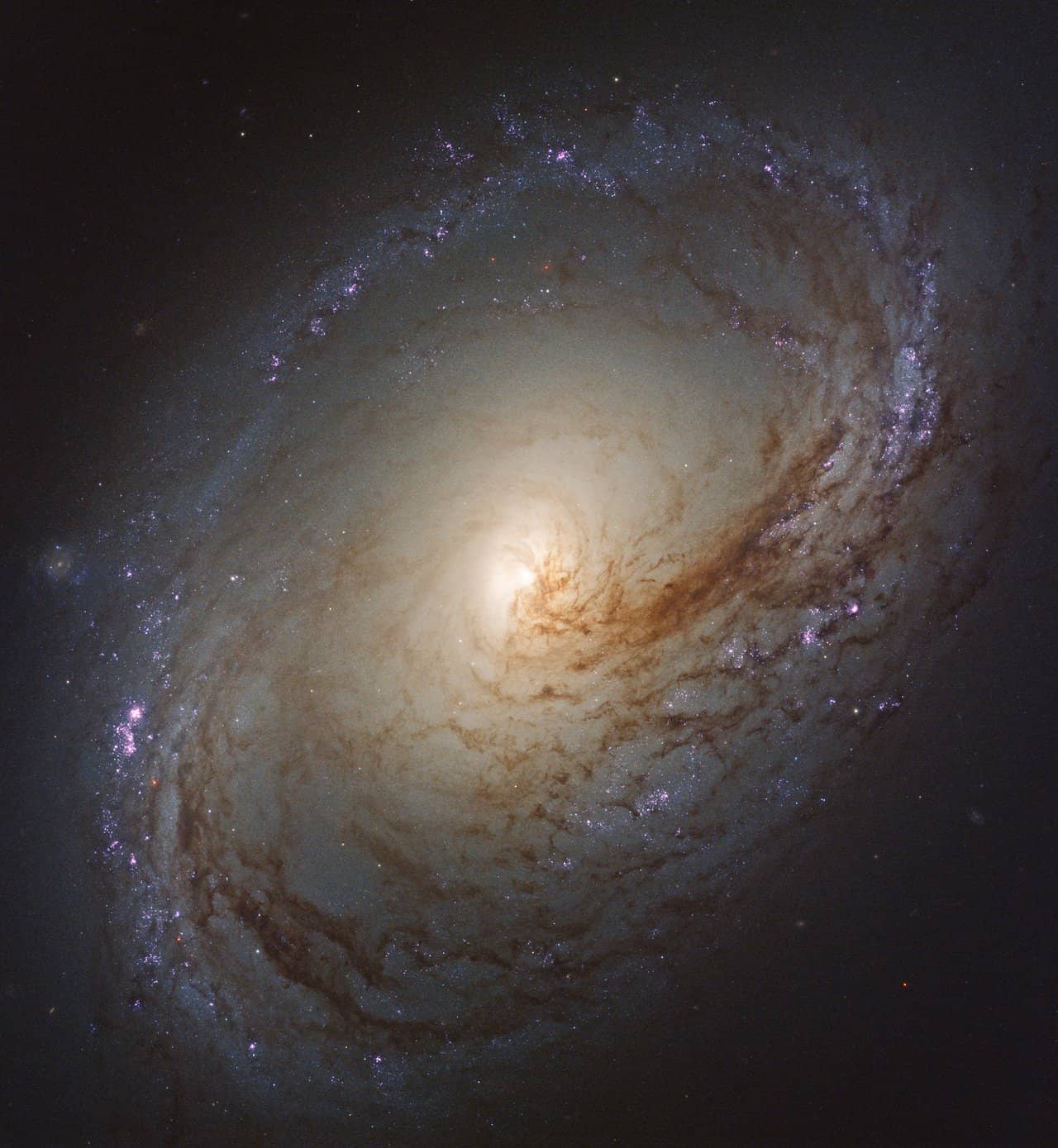

Why is Leo the Lion?
Leo Constellation looks like a lion. Its name in Latin means lion. In Greek mythology, the constellation of Leo is associated with the Nemean Lion. Hercules defeated him with his bare hands. Afterward, the lion was put in the sky as a remembrance of Hercules's achievement.
The Leonid's Meteor Shower
You can watch the Leonids meteor shower during mid-November every year. It is considered to be a massive shower with 15 meteors per hour. The meteors are either very bright or colorful. Their speed reaches 44 miles / 71 kilometers per second.
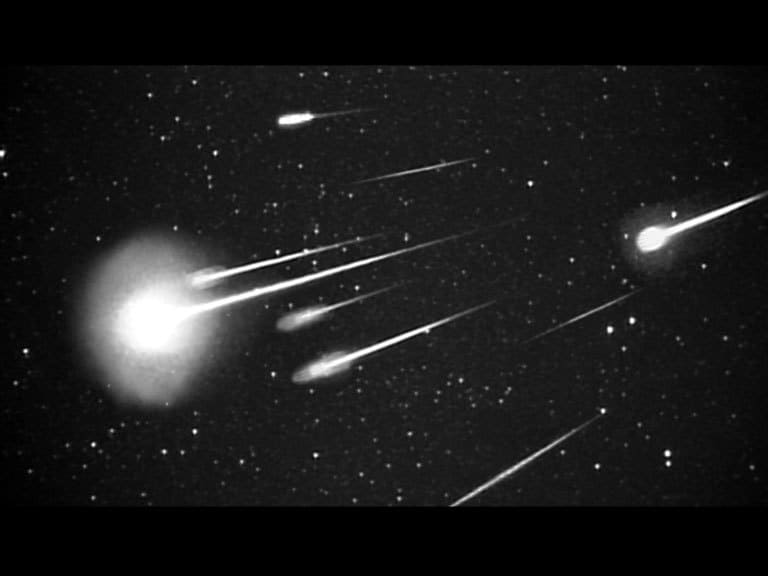

Once every 33 years, you can catch a Leonid storm with hundreds to thousands of meteors per hour.
Other Characteristics of the Constellation of Leo
The Sickle asterism in the constellation of Leo consists of six stars: Epsilon Leonis, Mu Leonis, Zeta Leonis, Gamma Leonis, Eta Leonis, and Alpha Leonis.
The lion's tail is made of Beta Leonis, and its body of Delta Leonis and Theta Leonis
In Babylonian astronomy, Leo Constellation was named UR.GU.LA, which means the "Great Lion." Regulus was known as "the star that stands at the Lion's breast."
There are many cool stars in Leo constellation such as : Denebola, Algieba, Zosma, Tay Leonis, Rasalas, CHertan, or Wolf 359.
Constellation of Leo Notes
- Leo is the 12th most prominent constellation in the sky out of a total of 88 modern constellations.
- Leo's constellation is amongst the easiest recognizable constellations in the sky.
- It is located in the zodiac belt, between the Crab and the Virgo constellations.
- The brightest star in Leo is the subgiant Regulus / Alpha Leonis, which has an apparent magnitude of 1.40. It can be seen with the naked eye.
- Many Messier objects, mainly galaxies, are situated in Leo.
- One of the most prominent meteor showers, the Leonids, appear to have their radiant in Leo's constellation.
Sources:
Image Sources:
- https://starregistration.net/media/wysiwyg/Constellations/Leo.png
- https://static01.nyt.com/images/2018/02/19/crosswords/19wordplay-lion/19wordplay-lion-superJumbo.jpg
- https://www.theguardian.pe.ca/media/photologue/photos/cache/atlantic-skies-can-you-find-leo-in-the-nights-sky-1_large.jpg
- https://nineplanets.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/Spring-Constellations.jpg
- https://i.pinimg.com/originals/5c/0b/ec/5c0bece73b787213d1813c5b0813ff85.jpg
- https://cdn.spacetelescope.org/archives/images/screen/heic1810e.jpg
- https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/system/content_pages/main_images/462_leonids_main.jpg
