In the grand scheme of the universe our little solar system is not considered huge. To ourselves however the magnitude of distances between our planets is impressive. In this article we are going to look at one of the planets in the solar system, find out more about it and try to answer the question: how far is Venus from Earth?
What Is Venus?
Venus is a rocky planet in our solar system which is the second closest to the Sun. It is Earth’s closest planetary neighbor and one of the four inner terrestrial planets. The structural similarities between Venus and the Earth have often earned it the moniker “Earth’s twin” although there are vast differences between the two rocky planets.

Venus’s Structure
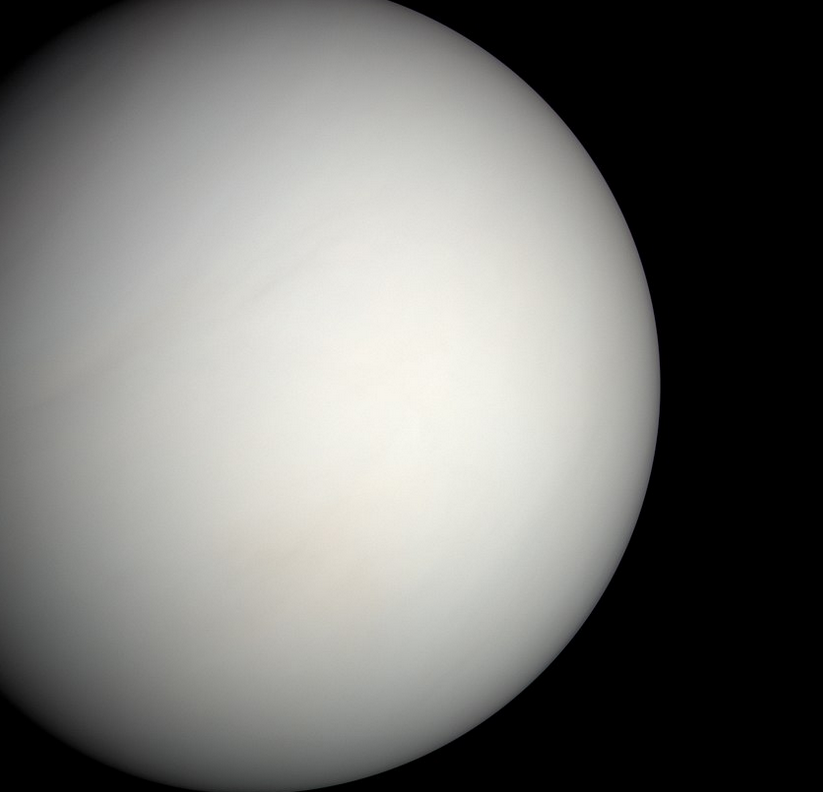
Venus has a dense toxic atmosphere which is heavy in carbon dioxide. The atmosphere on Venus is actually the thickest of all of our solar system’s rocky planets. Covered in dense yellow clouds of sulfuric acid which trap heat Venus is the hottest planet in our solar system. This is due to a very intense greenhouse effect and the close proximity to the sun.
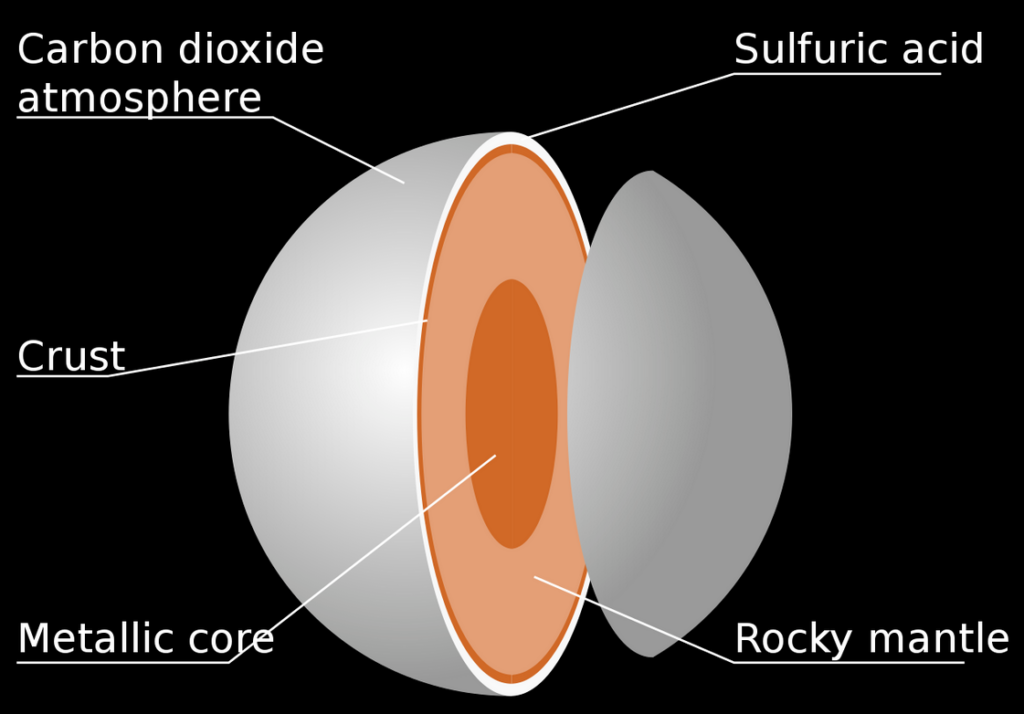
Venus’s diameter is 12,103.6 km (7,520.8 mi) which is only 638.4 km less than Earth’s. Its mass is roughly 81.5% of Earth’s which means in size the two planets are very similar. Its dense atmosphere consists of 96.5% carbon dioxide, with most of the rest being nitrogen.
Volcanoes
Much of the surface of Venus appears to have been carved by volcanic activity. It is in fact historically far more volcanic in nature than the Earth and has over 167 volcanoes wider than 100 kms. In excess of 85,000 volcanoes have been mapped on the planet.
The dense clouds of sulfur speak to the volcanic past and changes that have been mapped over the years indicate some level of volcanic activity still exists. It is postulated that the famous Venusian lightning may be connected to volcanic eruptions.
Internal Structure
It is hard to say with certainty what the internal structure of Venus looks like but its similarities to Earth may hint to a similar structure. This suggests the existence of a core, mantle and crust with the core likely being at least partially molten in nature. Although the core having solidified is not impossible.
Another big difference between Venus and Earth is the fact that there appears to be no indication of tectonic movement on Venus. This is possibly due to the crust being too strong and lack of oceans which would serve to soften it. As a result this slows the cooling of the planet and may be a cause of the lack of a magnetic field.
Does Venus Have Moons?
Venus is one of two planets in our solar system that has no natural satellites at all which is something that interests astronomers. There are three main ways that a planet gets a moon and early in the history of our solar system conditions were such that it is odd that Venus did not get at least one.
Prevailing thinking suggests that moons can be “captured” into orbit as they drift by the planet. This is likely what happened to Phobos and Deimos (near Mars). Alternatively an object may have smashed into the planet expelling fragments out beyond the planet’s atmosphere which eventually came together into a moon. Our own Moon is thought to have been created in this manner. Finally the moons might arise from the general accretion of matter. This is how the planets themselves were formed.
History of the Observation of Venus
Visual Observations
Its close proximity to Earth means that Venus has been a feature in our night sky since the two planets were created. Ancient human cultures would be well aware of this bright light in the sky as it would have been the third biggest object visible from Earth behind the Sun and the Moon.
The closeness of Venus however caused an issue which had ancient astronomers confused. It is not a continuous presence in the night sky as its closeness to the sun would cause it to disappear from our view on Earth for days at a time. It would then reappear in a different section of the sky leading to early beliefs that it was not a single entity. It was instead assumed to be two different stars.
Indications suggest that it was the ancient Sumerians who were the first to realize that the two perceived bodies were in fact one celestial object. To the Babylonians Venus was known as Ninsi’anna (divine lady, illumination of heaven).
It was in the second century that Almagest Ptolemy correctly theorized that Mercury and Venus were located between the Sun and Earth. It would take until the 12th century for an Andalusian astronomer Ibn Bajjah to observe two planets as the black spots on the face of the Sun. A century later astronomer Qotb al-Din Shirazi cast doubt on this observation claiming that Venus was not in transit during Ibn Bajjah’s lifetime.
Telescopic Observations
It was Italian physicist Galileo Galilei who first observed the planet Venus through a telescope in the early 17th century. Galileo found that it showed phases much like Earth’s Moon. They would vary from crescent to gibbous to full and vice versa.
It was observed that when Venus is furthest from the Sun in the sky, it shows up in a half-lit phase. However when it is closest to the Sun in the sky, it instead shows as a crescent or full phase. This could only be the case if Venus orbited the Sun. It was evident from this observation that the Ptolemaic geocentric model that the Solar System was concentric and centered on Earth was wrong.
Space Age Exploration
It was the Soviets in 1961 that made the first attempt to send a probe to Venus in the form of Venera 1. They however lost contact with the probe and the mission was a failure. It would be the United States Mariner 2 mission that would be the first to succeed.
Mariner 2 passed Venus on December 14th 1962 at 34,833 km above the surface gathering data as it traveled. Later in 1966 the Soviet probe Venera 3 became humanity’s first probe to impact another celestial body other than the Moon. Data could not be collected however as the probe had crash landed.
It was Venera 4 however that successfully released science equipment into Venus’s atmosphere leading to the discovery of the surface temperature and the makeup of the atmosphere.
How Far Is Venus from Earth?
With the exception of the Moon Venus is the Earth’s closest neighbor. It is roughly 61 million kilometers (38 million miles) away. Its proximity to Earth saw the United States and the Soviet Union sending frequent probes to Venus with the trip taking around 4 months.
Final Thoughts
The planet Venus is Earth’s closest neighbor which makes it one of the brightest objects seen in our night sky. A history of space probes sent to the planet since the 1960s attests to the closeness of the planet sometimes referred to as Earth’s twin.
