Algenib, designated as Gamma Pegasi, is the fourth brightest star in the constellation of Pegasus, the celestial winged-horse. Algenib is also one of the four stars that comprise the Great Square of Pegasus asterism.
Key Facts & Summary
- Algenib is located at around 390 light-years / 120 parsecs away from our Solar System.
- Algenib has an apparent magnitude of +2.84, and an absolute magnitude of -2.64.
- This star is a subgiant of spectral type B2 IV, appearing bluish-white in color.
- Algenib is also classified as a Beta Cephei variable, and a slowly pulsating B star, having brightness variations from magnitude +2.78 to +2.89 in a period of around 3,642 hours.
- The magnetic field of this star has been estimated at around 40 G.
- Algenib has a radial velocity of +4.1 km / +2.5 mi per second, and a rotational velocity of 0 km / 0 mi per second.
- This star is around 5,840 times brighter than our Sun.
- Algenib has around 8.9 solar masses and around 4.80 solar radii. It is bigger and much more massive than our Sun.
- The surface gravity has been estimated at 3.98 cgs.
- Algenib has surface average temperatures of around 21,179 K, thus it is much hotter than our Sun.
- Algenib is the fourth brightest star in the constellation of Pegasus, and it is the faintest star (due to its distance) of the Great Square of Pegasus asterism, which is comprised out of Algenib (Gamma Pegasi), Markab (Alpha Pegasi), Scheat (Beta Pegasi), and Alpheratz (Alpha Andromedae).
- Algenib is the largest and most massive star of the Great Square of Pegasus asterism.
- This star is quite young, having an estimated age of around 18.7 million years, much younger than our Sun.
- The constellation of Pegasus is the 7th largest in the sky.
γ Pegasi
Gamma Pegasi was formally named Algenib by the IAU in 2016. The same name was also used for Alpha Pegasi, but it changed to Mirfak, also in 2016.

The name “Algenib” comes from the Arabic “al-janb” – and it means “the side”. Algenib’s position in the sky marks one of the celestial horse’s wings.
Formation
Algenib formed around 18.7 million years ago from an interstellar medium of gas and dust. Gravity pulled the swirling gas and dust together, and when it reached the right temperature, the fourth brighter star in Pegasus, Algenib, was born.
Distance, Size, and Mass
Algenib / Gamma Pegasi is located at around 390 light-years / 120 parsecs away from the Sun. It is visible to the naked eye under the right conditions.

Algenib is larger and more massive than our Sun, having 8.9 solar masses, or 890% of our Sun’s mass, and 4.80 solar radii, or 480% of our Sun’s radius. It is thus more than 10 times bigger than our Sun.
Other Characteristics
Algenib is a bluish-white subgiant of spectral type B2 IV. It has almost exhausted its hydrogen supplies in its core, and it slowly evolves away from the main-sequence, with its radius constantly expanding.
Algenib is 5,840 times brighter than our Sun, having an apparent magnitude of +2.84, and an absolute magnitude of -2.64. This star is classified as a Beta Cephei variable, its brightness varies from magnitude 2.78 to 2.89 in a period of around 3,642 hours.

It is also classified as a pulsating B star since it shows other pulsation frequencies that are similar to those types of stars.
Algenib has surface temperatures of around 21,179 K, it is thus 3.6 times hotter than our Sun. This star has a radial velocity of +4.1 km / +2.5 mi per second, and it has a very slow rotational velocity since it was estimated at 0 km / 0 mi per second. This is rather unusual, and some suggest that the star isn’t rotating so slowly, but rather, we are viewing it almost pole-on.
Location
Algenib is located in the constellation of Pegasus, the celestial winged horse. It is the fourth brightest star in the constellation and it is the star that marks the southeast corner of the Great Square of Pegasus asterism.
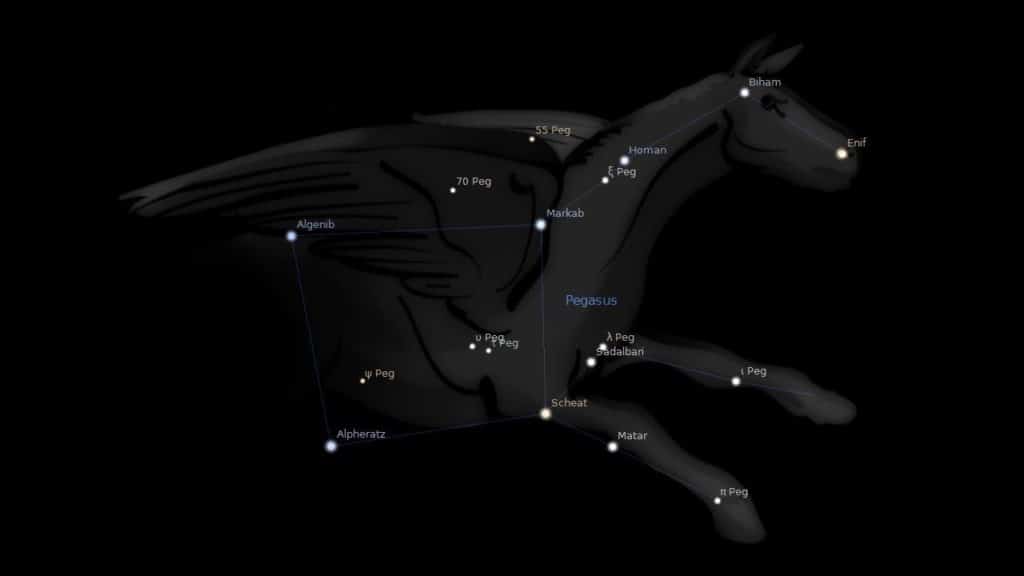
Algenib is the faintest out of the four stars that make up this asterism, the other three stars are Markab (Alpha Pegasi), Scheat (Beta Pegasi), and Alpheratz (Alpha Andromedae). It would be much brighter, but it has to be noted that Algenib is also the farthest star in this asterism, and it is the most massive and largest of all four.
The Great Square of Pegasus can be found using the bright stars in the Cassiopeia constellation, that make up the W pattern. A line extended from Segin through Ruchbah, the stars on the left side of the W, points directly to the Great Square of Pegasus.
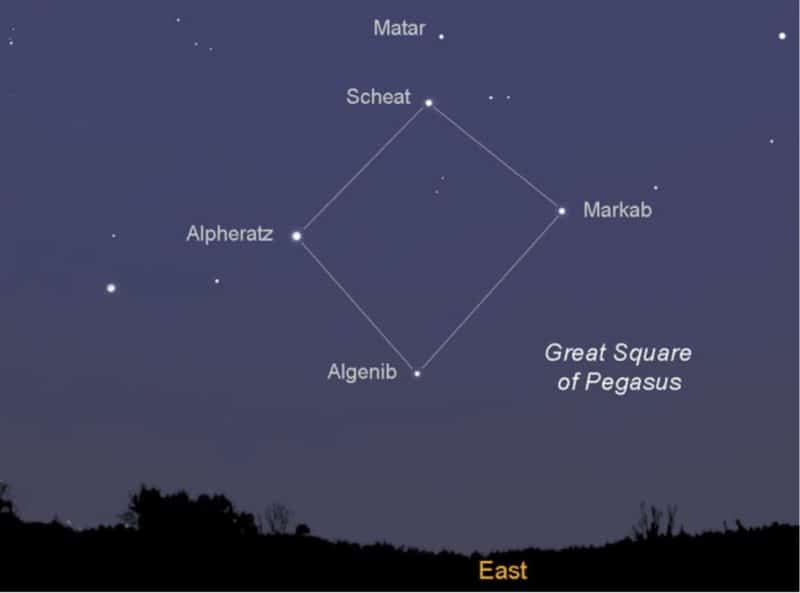
This asterism, along with its stars, can be used to find numerous deep-sky objects, Algenib, for example, can be used to find the irregular galaxy NGC 14.
Algenib is easy to spot since it marks the tip of the wing of the celestial horse. The constellation of Pegasus is among the first 48 Greek constellations, listed by Ptolemy, in his 2nd century Almagest.
Pegasus is now one of the 88 modern constellations, being the 7th largest in the sky, stretching for around 1,121 square degrees. It is the third-largest northern constellation after Ursa Major and Hercules.
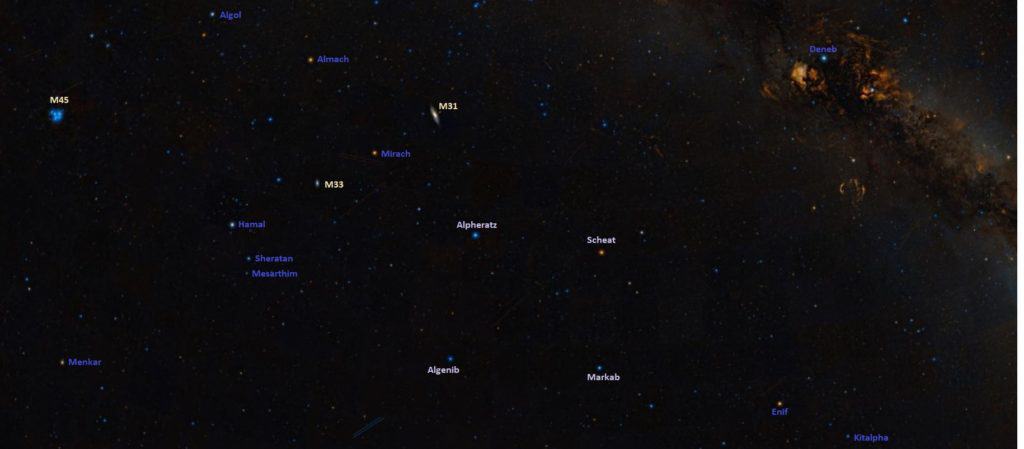

Apart from the bright stars in the Great Square asterism, Pegasus is known for its deep-sky objects, such as the Great Pegasus Cluster/ Messier 15, which is among the brightest and oldest clusters in our galaxy, the spiral galaxy NGC 7331, the unbarred galaxy NGC 7742, the Propeller Galaxy, the edge-on spiral galaxy NGC 7814, the compact galaxy group HCG 92, or the gravitationally lensed quasar known as Einstein’s Cross.
The best time of the year to observe Algenib, the bright stars and deep-sky objects in Pegasus, is during October when the constellation is prominent in the sky.
The Future
Algenib will continue to exist for millions of years, however, one day the star will evolve into a white dwarf. Algenib is not massive enough to explode as a supernova.
Did you know?
- Algenib is one of the Three Guides that mark the prime meridian of the heavens, the other two being Scheat and Alpheratz.
- The Chinese know Gamma Pegasi / Algenib, as Bixiu yi – the First Star of Wall – The Wall mansion is formed by Algenib and Alpheratz / Alpha Andromedae – the brightest star in Andromeda. It is one of the seven mansions of the Black Tortoise.
- In Hindu astronomy, the asterism comprised of Algenib and Alpheratz is known as Uttara Bhadrapada or Urrtati – which is the 26th nakshatra (lunar mansion) in Hindu astrology.
Sources:
Image sources:
- https://www.star-facts.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/Algenib-1240×620.jpg?189db0&189db0
- https://tarot-astrology.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/algenib-fixed-star-gamma-pegasi.jpg
- https://www.cloudynights.com/uploads/gallery/album_8287/med_gallery_261696_8287_264502.jpg
- https://i.pinimg.com/originals/58/84/4c/58844cc40b2b9785386b16c79be9b618.jpg
- https://earthsky.org/upl/2017/09/great-square-star-names-astrobob-e1511187972965.jpg
- https://www.star-facts.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/Great-Square-of-Pegasus-location.jpg?189db0&189db0
